How to Design Tables with Relationships in Access for Beginners
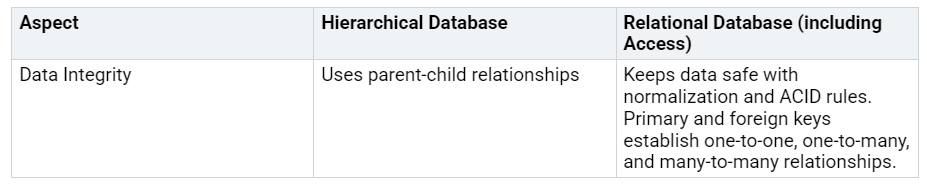
When you design tables in Access, you create organized spaces for your data. You choose primary keys to assign each record a unique ID. You link tables through relationships, ensuring your data remains accurate and well-structured. Relational databases like Access rely on keys and rules to protect data integrity, outperforming older systems.
You can lear…