How to Use .NET MAUI for an AI-Powered Personal Companion Experience
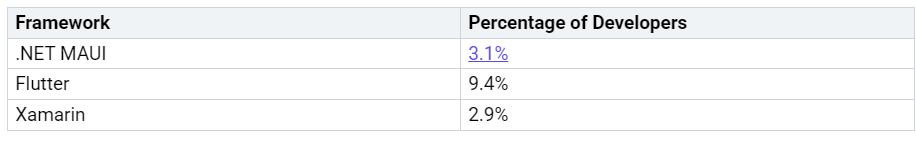
Ever thought about having your own AI-Powered Personal Companion? You can make one that works on your phone, tablet, or computer with .NET MAUI. Many developers pick other frameworks, but .NET MAUI still has loyal fans:
People use these apps for lots of reasons. Some talk about mental health, some get help with schoolwork, and others track their daily ha…