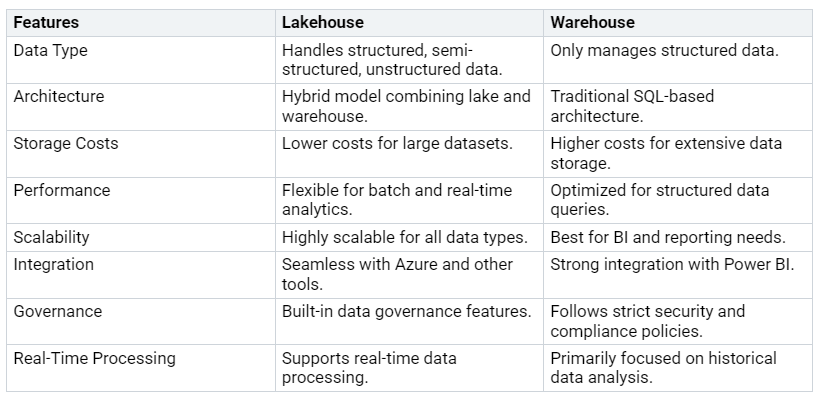
Comparing Lakehouse and Warehouse Features
Explore the key differences between Lakehouse and Warehouse in Microsoft Fabric.
In Microsoft Fabric, the comparison of Lakehouse vs Warehouse highlights their distinct roles in data management. A Lakehouse can handle all data types, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, while a Warehouse …