Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Ambient Agents Using Azure AI Foundry
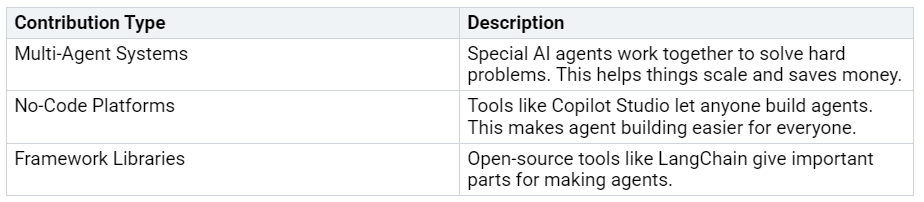
You can now make Ambient Agents. These agents talk to users only when needed. They act based on signals from the environment. Azure AI Foundry and LangChain help you do this. They support multi-agent systems, no-code platforms, and open-source libraries. These tools let agents work together. They help finish hard tasks.
You can use Deep Research Agent, A…