Optimizing Dataverse performance is crucial for providing users with a smooth experience. Many people assume that too much data is the root cause of performance issues. However, a significant number of problems stem from complicated relationships and poor schema design. For instance, slow response times can occur when loading forms that involve numerous related tables. As your data grows, these slowdowns can significantly impact how quickly users access information. Understanding these challenges is the first step toward creating efficient and scalable applications.
Key Takeaways
Learn how users access data to make things faster. Look at common questions to create better schemas and indexing plans.
Make your database schema better by mixing normalization and speed. Regularly delete unused fields to keep your schema neat and effective.
Use indexing smartly to make queries faster. Focus on fields that are often searched and limit auto-indexing to keep the system running well.
Plan for growth from the beginning. Set rules and make sure your system can handle more users.
Keep checking performance numbers. Use tools like Power BI and Azure Application Insights to find ways to improve.
Understanding Data Access Patterns
Knowing how users use your Dataverse apps is important for better performance. You might think that having a lot of data causes slowdowns. But often, bad data access patterns are the real problem.
Analyzing User Queries
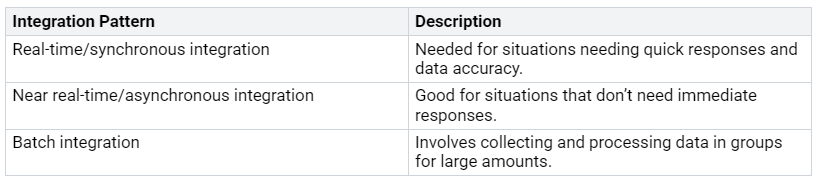
First, look at the types of queries users make. Common queries are searching for records, filtering data, and gathering information. For example, a user may want to see all customer records made last month. This needs good indexing and schema design to get results fast.
Consider this table showing common data access patterns in enterprise Dataverse setups:
Identifying Common Access Patterns
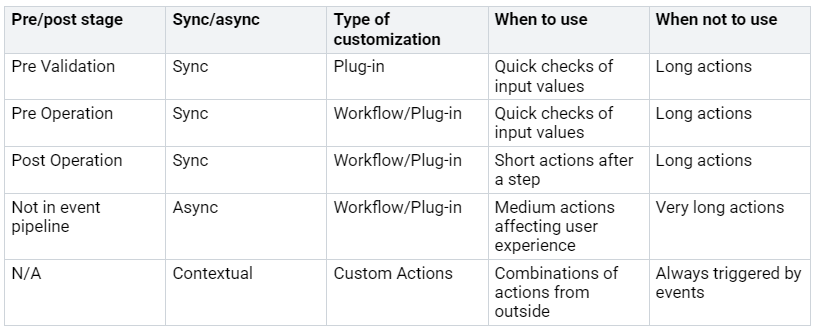
Next, find the common access patterns in your app. These patterns can affect how you design your schema. For example, if users often do pre-validation checks, you may want to use synchronous plug-ins for quick checks of input values.
The table below shows different access patterns and when to use them:
By looking at user queries and finding these common access patterns, you can make smart choices about schema design and indexing. This will help you create faster and more dependable Dataverse apps.
Optimize Database Schema
Making your database schema better is important for improving Dataverse performance. A good schema can make queries faster and improve how well everything works. But, you need to find a balance between normalization and performance needs.
Normalization vs. Performance
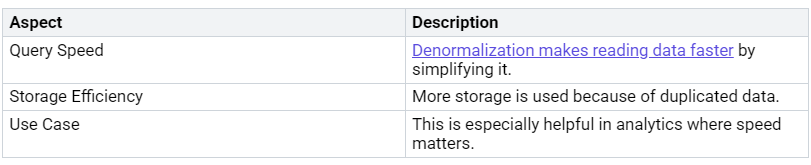
Normalization helps reduce data duplication by organizing data into related tables. This can make data more accurate but might slow down queries because of the extra joins needed. Think of your schema like a filing cabinet. A neat cabinet helps you find papers quickly. But if you make too many folders, you might waste time looking instead of grabbing what you need.
Keep these points in mind when thinking about normalization:
Sometimes, denormalization might be the better option. It can cut down on the number of joins in queries, making them faster. But, you should think about the extra storage costs from having duplicate data.
Managing Unused Fields
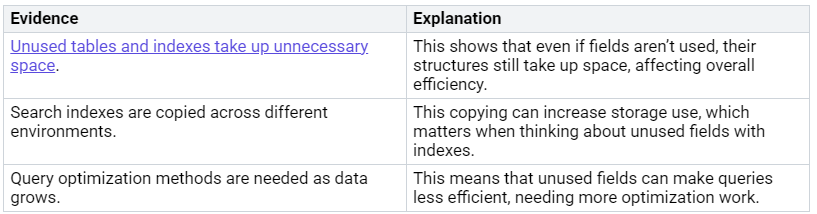
Unused fields can make your schema messy and hurt performance. Even if you don’t use some fields, they still take up space and can make queries harder to optimize.
Here are some important points about unused fields:
To improve your database schema, check and remove unused fields regularly. This not only saves space but also makes your schema simpler, making it easier to manage and query.
By making smart changes to your schema and focusing on optimization strategies, you can greatly improve the performance of your Dataverse applications.
Improve Query Performance with Indexing
Indexing is very important for making your Dataverse apps work better. When you use indexes wisely, you can make queries faster and improve how the system responds. But, it’s important to know the different types of indexes and follow best practices to get the most out of them.
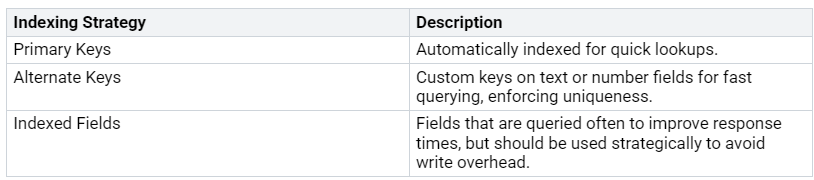
Types of Indexes
In Dataverse, there are different types of indexes that can help you make queries faster:
Primary Keys: These indexes are made automatically for each table. They help find data quickly and keep it unique.
Alternate Keys: You can create custom keys on text or number fields. These keys help with fast searches and keep data unique, which is good for checking data.
Indexed Fields: These are fields you search often. Indexing these fields can make responses quicker. But be careful; too many indexes can slow down writing data.
Using the right mix of these indexes can help you set up your database for the best performance.
Best Practices for Indexing
While indexing can really help with query speed, it’s important to follow some best practices to avoid problems. Here are some key tips:
Limit Auto-Indexing: Auto-indexing can sometimes slow things down when you add or change data. This happens because it puts extra work on the system. Instead, try manual indexing for better control over how many indexes you have. This can help reduce unnecessary indexes and improve performance.
Evaluate Index Usage Regularly: As your app changes, so do how people access data. Check your indexes often to make sure they are still useful. If some indexes are not needed anymore, removing them can help your database run smoother.
Focus on Frequently Queried Fields: When choosing which fields to index, pick the ones users search for the most. This way, you can improve query speed without overloading the system with too many indexes.
Monitor System Resource Consumption: Indexing affects how much system resources are used. Things like new features, data size, and changes in usage can change index size. Keep track of these things to keep performance high.
Here’s a summary of good indexing strategies for large Dataverse tables:
By following these best practices, you can use indexes well to make query performance better in your Dataverse apps.
Case Study: Query Time Reduction
Imagine a company that had slow query times because a table was not indexed well. After looking at how users accessed data, they found that people often searched for customer records by last names. The team decided to add indexes on the last name field.
As a result, they cut query times from several seconds to just milliseconds. This change not only made users happier but also helped everyone work better. These examples show how important smart indexing is for getting the best performance.
Scalability and Proactive Architecture
Scalability is very important for any Dataverse app. You need to plan for production loads from the beginning. As more users join, your app should handle the extra demand without slowing down. Here are some important things to think about for scaling Dataverse well:
Governance: Set up rules to manage growth. This helps control how your user base grows from small to large.
Architecture Support: Your basic setup must support growth. Simple solutions might not work when demand increases.
Integration with Azure: Using Dataverse with Azure makes it stronger and more scalable. This is key for big business performance.
By focusing on these points, you can create a strong base that can grow in the future.
Tools for Proactive Management
Knowing what causes performance problems in Dataverse is key for proactive management. Long transactions, database blocking, and complex queries can hurt scalability. Fixing these problems with optimization methods makes Dataverse work better and scale well.
Here are some tools and strategies you can use for proactive management:
Enable Auditing: Keep track of user actions and data changes in Dataverse. This helps you spot problems early.
Set Up Validation Rules: Make sure data is accurate and consistent by setting clear rules.
Establish Naming Conventions: Use clear names for entities, fields, and relationships. This makes things clearer and less confusing.
Create Data Policies: Set rules for keeping, archiving, and deleting data. This keeps your database clean and efficient.
Utilize Azure AD: Use Azure Active Directory for managing identities and access. This controls who can access Dataverse environments well.
Also, think about these best practices to keep performance high:
Split large transactions into smaller, easier parts.
Use asynchronous processing for big tasks.
Limit the data pulled in plug-ins to just what you need.
Use Optimistic Concurrency Control to prevent database blocking.
Improve FetchXML queries by avoiding extra joins.
By using these tools and strategies, you can stop performance drops and keep a responsive Dataverse environment. Proactive management not only improves user experience but also builds trust in your apps.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Keeping an eye on performance and making improvements is very important for your Dataverse apps. Regular checks help you find and fix problems before they affect users. By watching certain metrics, you can learn how well your apps work and where you can make them better.
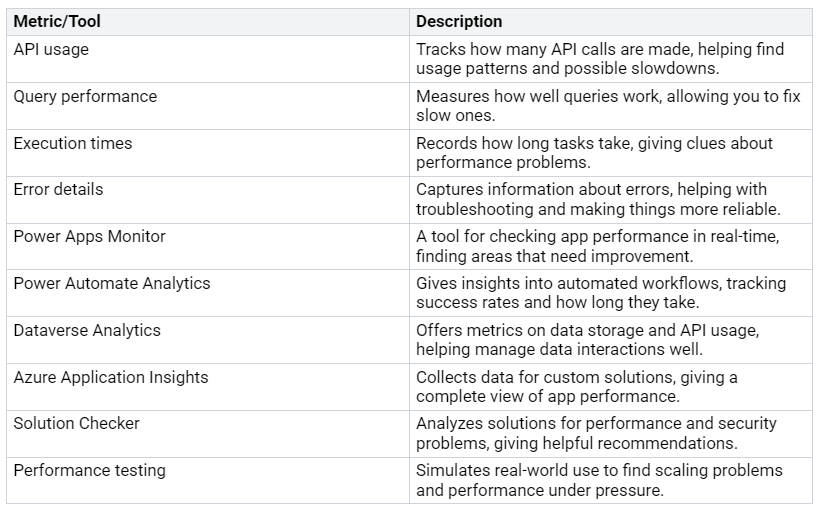
Performance Metrics to Track
You should pay attention to some key performance metrics to improve your Dataverse environment. Here’s a table that lists the most important metrics:
By tracking these metrics, you can find areas to improve and boost overall performance.
Tools for Monitoring Dataverse Performance
Using the right tools can really help you monitor performance in real-time. Here are some tools you should consider:
Microsoft Dataverse analytics: Gives interactive metrics on plug-in performance.
Plug-in dashboard: Shows metrics like average execution time, failures, and most active plug-ins. You can find this in the Power Platform Admin Center under Analytics > Dataverse > Plug-ins.
Power BI: Connects with Microsoft Lists and Dataverse to create custom visuals and reports, making data easier to see.
Azure Application Insights: Gathers and analyzes data from Dataverse plugins, helping find performance issues.
By using these tools, you can get useful insights into how your apps perform and make smart choices for improvements.
Making Dataverse work better is very important for creating fast and dependable apps. You should think of performance as a key part of your design. Focus on making simple schemas, planning indexes early, and creating smart relationships.
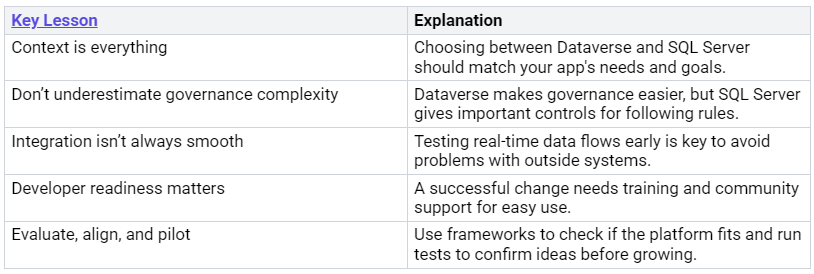
Here are some important lessons from case studies about improving Dataverse performance:
By using these tips, you can improve user experience and build trust in your apps. 🌟
FAQ
What is the best way to improve Dataverse performance?
To make Dataverse work better, focus on improving your schema. Use good indexing and plan for growth. Check performance metrics often and change your design based on how users access data.
How often should I review my Dataverse schema?
You should check your schema regularly, about every few months. This helps you find unused fields and improve relationships. It keeps your database working well as your app changes.
What tools can I use for monitoring Dataverse performance?
You can use tools like Microsoft Dataverse Analytics, Power BI, and Azure Application Insights. These tools give you information about performance metrics and help you find areas to improve.
How does indexing affect write performance?
Indexing makes reading data faster, but it can slow down writing. Each time you add or change data, the system must update the indexes too. Finding a balance is important.
What are the risks of over-normalization in Dataverse?
Over-normalization can cause too many joins in queries, which may slow things down. Try to find a balance between normalization and denormalization. This helps speed up queries without losing data quality.