The Win32 app method is the superior choice for packaging applications within Microsoft Intune, offering unparalleled flexibility. This approach provides numerous options, adeptly handling complex installations and custom scripts. It supports a broader range of applications compared to basic MSI files, built-in apps, or simple Winget options. You can even incorporate executable files. This guide will teach you Win32 app packaging, streamlining your Intune deployment process and simplifying the deployment of any application with Intune.
Key Takeaways
Win32 apps are the best way to put apps on Microsoft Intune. They can handle hard installations. They also work better with special scripts.
Use the
IntuneWinAppUtiltool. It puts your app files into a.intunewinformat. Intune needs this file type. This is for Win32 app deployments.Always find silent install commands. Also find uninstall commands for your apps. Intune puts apps on computers without anyone clicking. So, these commands are very important.
Try Win32 apps on a few people first. Do this before giving them to everyone. Look at the
IntuneManagementExtension.logfile. It is on the device. This helps fix any problems with installing.Make Intune app deployment better. Use Delivery Optimization (DO). DO makes downloads faster. It also uses less internet data. This is good for big apps.
Win32 App Deployment Benefits
Win32 apps are best. They are strong and flexible. They are better than simple MSI files. They are better than EXE installers. They are better than Microsoft Store apps. You control how apps go on devices.
Win32 App Key Benefits
Win32 apps give you more control. They are flexible for managing apps. LOB apps use one file. Win32 apps use many file types. They use EXEs. They handle many files. This makes installs easier. You can deploy big install files. LOB apps have size limits. Win32 apps have more options. They find other apps. They use dependencies. They use supersedence. LOB apps do not have these. You can customize more. You control how apps install.
Win32 App Use Cases
Win32 apps are good for hard installs. These installs need other things. You can use them for apps. These apps need parts installed first. This method uses custom scripts. It uses parameters. This gives more customization. You can use PowerShell scripts. These are for Win32 app installs. They are not like old commands. You control install logic. You control prerequisites. You control error handling. It fixes old command limits. You can install based on conditions. You can check things before install. You can make system changes. This makes Win32 deployment flexible. It is for hard situations. You can deploy custom apps. You can deploy non-packaged apps. These are like folders with files. This lets you deploy apps with Intune. These apps might be hard otherwise.
Win32 App Packaging Prerequisites
You need to get some tools. You also need to get your files ready. Do this before you package apps for Intune. This helps your deployment go well.
Required Tools
You need one main tool. It is for Win32 app packaging. It is called IntuneWinAppUtil. This tool changes your app files. It makes them into .intunewin format. Intune needs this format. You can get this tool from GitHub. Look for the Microsoft Win32 Content Prep Tool. Click ‘Code’. Then click ‘Download ZIP’. This tool is key. It makes the win32 package.
Source File Preparation
Get your app’s files ready. Put all install files in one folder. This includes msi or exe installers. Also add any scripts or data files. This folder is for the IntuneWinAppUtil tool. A neat folder makes packaging easy. For example, put an exe installer and a PowerShell script in the same folder.
Install/Uninstall Commands
You must find the silent commands. These are for installing and uninstalling your application. Intune installs apps without you. So, silent commands are very important.
MSI Installers (.msi files): These often use
/quietor/qn. You can see all options. Typemsiexec.exe /?in PowerShell or CMD.EXE Installers (.exe files): Silent commands for
exefiles are different. Developers choose these commands. Common ones are/silent,/s, or/S. Someexeinstallers may not install silently.
Think about these commands. They help with silent actions:
/SILENTor/VERYSILENT: These stop pop-up messages./VERYSILENTalso hides the uninstall window./SUPPRESSMSGBOXES: This stops message boxes. Use it with/SILENTor/VERYSILENT./NORESTART: This stops your computer from restarting. This is true even if a restart is needed.
Knowing these commands helps you. You can set up Intune correctly. It will install apps silently.
Package Win32 Apps with IntuneWinAppUtil
You have your application files ready. Now, you need to package them. The IntuneWinAppUtil tool helps you. It turns your application files into one .intunewin file. Microsoft Intune uses this file. It is for deployment. This step is key. It helps deploy win32 apps.
IntuneWinAppUtil Download
First, get the IntuneWinAppUtil tool. It is also called the Microsoft Win32 Content Prep Tool. You can download it from GitHub. Go to the official Microsoft page. Find the newest version. Download the ZIP file. Unzip it to a folder. You will see IntuneWinAppUtil.exe there.
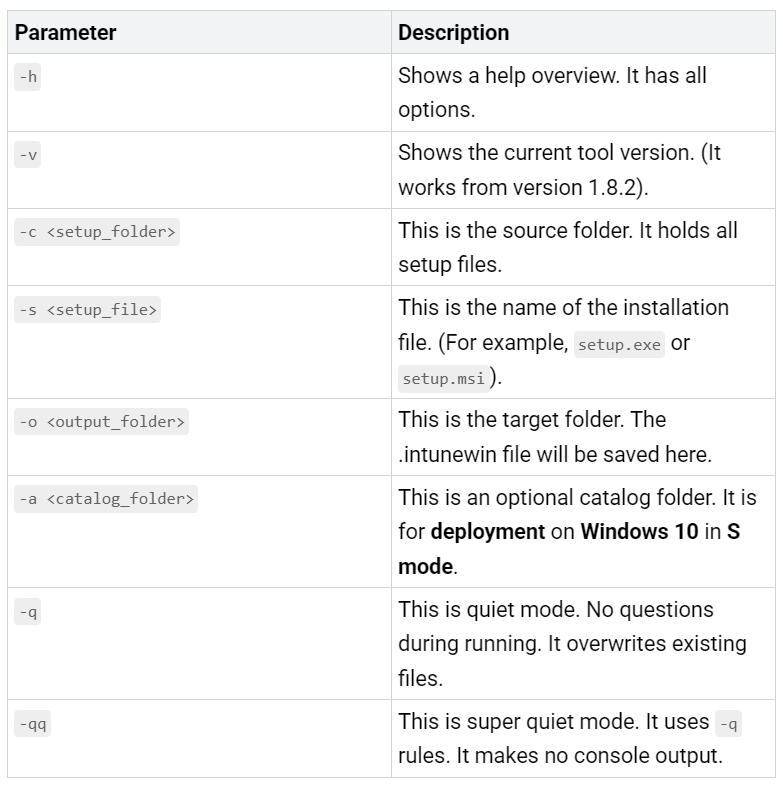
IntuneWinAppUtil Command Usage
Before using the tool, sort your files. Make a folder for each application. Put the installer file there. This means exe or msi files. Add any other scripts or data files. This makes packaging easy. The IntuneWinAppUtil tool gathers all data. It takes it from your chosen folder. It keeps the original file structure. Do not point the tool at a messy folder. For example, do not use your Downloads folder. The tool will try to wrap everything. This can make your .intunewin file too big. It will have unwanted software.
You can use IntuneWinAppUtil in two ways:
Interactive Mode:
Open Command Prompt or PowerShell.
Go to the folder. This is where
IntuneWinAppUtil.exeis.Run
IntuneWinAppUtil.exe.The tool will ask questions. You will give the source folder. You will give the setup file name. You will give the output folder. You can leave the catalog folder empty. This is true for most cases.
Direct Command-line Call: You can also run the tool. Put all settings in one command. This is faster for repeated work. Here are the settings you can use:
Here are some examples:
IntuneWinAppUtil.exe -c “C:\Install\7Zip” -s “7zSetup.exe” -o “C:\Output”IntuneWinAppUtil.exe -c “C:\Installers\Notepad ++” -s “npp.exe” -o “C:\IntunePackages” -q
This tool can handle big applications. It supports apps up to 30 GB. It is made to deploy complex Windows apps. This includes apps with exe files. It includes many msi files. It includes MST files. It includes batch files. It uses the Intune Management Extension for deployment.
Creating the .intunewin File
When you run IntuneWinAppUtil, it does many steps. It makes your .intunewin file. This packaging process makes your app ready for Intune.
The tool squeezes your source folder. It puts this data into a subfolder. This folder is named ‘Contents’.
Then, it locks this squeezed file.
Next, it makes a SHA256 hash. This is for safety.
It creates a
Detection.xmlfile. This file goes into a ‘Metadata’ subfolder.Finally, it squeezes the whole working folder. This makes your final
.intunewinfile.
The .intunewin file is like a special .zip file. Inside, you will find:
IntuneWinPackage\Contents\A locked
.zipfile. This file holds your original source folder.
Metadata\Detection.xml. This file has important unlock info. It has other details too.
The inner IntunePackage.intunewin file is a .zip file. It is locked using AES-256. It also uses keyed hashing. This is called HMAC-SHA256. This method is called Authenticated Encryption. The Detection.xml file stores the keys. These keys are needed for this process.
If you need to check an .intunewin file, you can use a tool. It is called IntuneWinAppUtilDecoder. Oliver Kieselbach made this tool. It can pull out and unlock the contents. It reads the EncryptionInfo. This is from Detection.xml. This gives it the key. It also gives it the starting code. Then, it unlocks the inner content zip file. You can find this tool on GitHub. You use it like this:
IntuneWinAppUtilDecoder.exe <FullPathToIntunewinFile> [/s | /silent]
[/key:base64encodedKey /iv:base64encodedIV]
This process makes sure your win32 apps are safe. They are ready for deployment.
Deploy Win32 Apps in Intune
You packaged your application. Now, put it into Intune. This part shows you how. You will upload your .intunewin file. You will set up the details. Then, your application is ready for users.
Uploading the .intunewin File
First, add your packaged application to Microsoft Intune. This is the start for any Intune deployment.
Go to the Intune admin portal.
Find Apps > All Apps.
Click Add.
Pick Windows app (Win32). This is from the App type list.
Click Select.
Click Select App Package File.
Click the Blue Folder icon.
Find your
.intunewinfile. Select it.Click Open, then OK.
Be careful with your internet speed. This is true when uploading big .intunewin files. A slow speed can stop uploads. You might see a 15-minute timeout. This often happens. It is because of login token problems. The token does not refresh. This happens during a long upload. If you get a ‘403 Server failed to authenticate the request’ error, try faster internet. This helps the app upload fast. It prevents errors.
Configuring the Intune Win32 Application
You uploaded the file. Now, set up the Intune Win32 application details. These settings tell Intune how to install your app. They also tell it how to manage it.
App Information: Fill in details for the Win32 app. Users will see this in the Company Portal. Make it clear and helpful.
Program Settings: Set the install and uninstall commands. For example, use
msiexec /i “[APP_NAME.msi]” /qnto install. Usemsiexec /x “{APP_DETECTION_CODE}” /qnto uninstall.Requirements: Say what kind of computer it needs. This means 32bit, 64bit, or both. Set the oldest operating system version. For example, Windows 10 1607. You can also add other needs. These are like disk space.
Detection Rules: Set these rules yourself. Often, you pick MSI as the rule type. The MSI product code usually fills itself in. You can also check the MSI product version. Pick an operator, like ‘Greater than or equal to’. Then, pick a specific version number.
Defining Requirements and Detection
You must set clear rules. These are for requirements and detection. This makes sure your Intune Win32 application installs right. It also checks if the app is on devices.
Common rules for Win32 applications include:
Operating system architecture: Say if the app needs x64 or x86.
Minimum operating system: Set the oldest OS version it works on.
Disk space required (MB): Say how much free disk space is needed.
Physical memory required (MB): Say how much RAM is needed.
Minimum number of logical processors required: Set the fewest CPU cores needed.
Minimum CPU speed required (MHz): Say the slowest processor speed.
You can also use file system information. Or use registry values. These are for more specific needs. PowerShell scripts are best. This is true when other ways are not enough.
For detection rules, you have choices:
MSI: This finds an application. It uses its MSI product code. You can also check its product version.
File: This finds an application. It looks for a certain file or folder. You can check its date, version, or size.
Registry: This finds an app. It checks a registry setting. You can look for a key. You can look for a value’s string, number, or version.
Custom script: This lets you use smart detection. The app is found. This is true if the script ends with 0. It must also show some output.
Make good detection rules. Make sure you have correct facts. Keep up with new trends. Test your rules often. Check how many apps are found. Check for wrong detections. This helps you fix mistakes. Work with other teams. Change your rules often. This makes sure your rules fit your goals.
Assigning the Application
You set up your Intune Win32 application. Now, give it to user or device groups. This decides who gets the application for deployment.
Required: Intune puts the app on devices automatically. Or for certain users.
Available for enrolled devices: Users can get the app. They use the Company Portal.
You can pick security groups. These groups can have users or devices. For apps on each machine, use device groups. These apps install for the whole system. This works well during the Enrollment Status Page (ESP). It makes sure the app is there for everyone. For Company Portal apps, use user groups. The portal is for users. But Win32 apps are flexible. You can choose device-level or user-level. Device-level affects all users on the device. It writes to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM). User-level follows the user. This is true across devices. It writes to HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU).
You can also set up supersedence. This lets you change or update software. You pick the old deployment package. You can choose to remove the old one. This is good for changing one app. You can replace it with a new one.
Optimizing Intune Application Deployment
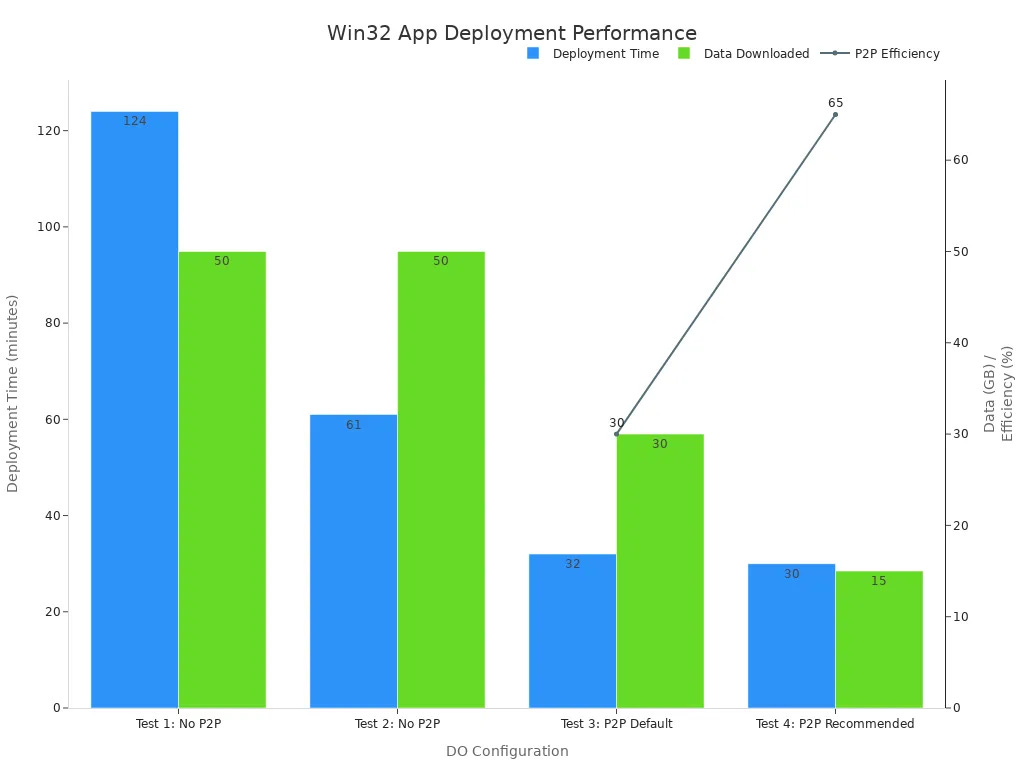
You deploy Win32 apps. Especially big ones. Making downloads fast is important. Delivery Optimization (DO) helps with this. DO is a cloud tool. It downloads HTTP files. It lets Windows devices get big files. They come from other places. These places include other devices. They can be on the same network. Or a special storage server. This uses less internet data.
You can set DO options. This makes it work better:
DOMaxCacheSize: This sets how much disk space DO can use. It is a percentage.DOMaxCacheAge: This makes content last longer. Devices can then share files better.DOMinRAMAllowedToPeer: This sets the least RAM needed for sharing.DODelayBackgroundDownloadFromHttpandDODelayForegroundDownloadFromHttp: These wait before downloading from HTTP. This gives more time. It helps download from other devices or a server.
DO greatly lowers internet download needs. It makes delivery faster. This is true for many Microsoft things. This includes Intune application deployment. Companies save a lot of internet data. Often 70-90%. With Connected Cache, savings can be 98-99%. If only devices share, few download from the internet. Others get files from the local network. This chart shows how DO makes deployment better:
This makes your application deployments work well.
Test and Troubleshoot Win32 Apps
Test Group Deployment
Always test your Win32 apps. Do this before a full rollout. Use a small group of users first. This is a good idea. Check the app. Then, deploy it to more people. Test in steps. First, give the new app to your IT team. Get their thoughts. See if it installs well. Check if it works. Next, pick some regular users. Watch for problems they report. Last, send it to all users. This step-by-step way helps. It finds problems early. It stops issues for everyone.
Installation Verification
You deploy your Win32 apps. After that, check the install. See if the device meets app needs. Make sure detection rules are right. Check for a good network. This is for downloading the app. For fixing problems, look at logs. Check IntuneManagementExtension.log. It has error messages. This log is very important. Find it at C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension\Logs. It is on the Windows device. Test on some devices first. This helps find and fix issues early.
Common Deployment Errors
You may see errors. This happens when installing apps. One error is 0x87D1041C. This means the app installed. But Intune did not see it. This often means a typo. It is in the app’s detection. To find the problem, check logs. Use Intune’s ‘Collect Diagnostics’. This gets logs from far away. Then, fix the detection. Do this in the Intune admin center. Other problems are 32-bit/64-bit issues. Intune runs apps as 32-bit. This is the default. Use %SystemRoot%\sysnative for 64-bit scripts. Network rules can block Intune. Work with your security team. Let Intune reach needed places. Delivery Optimization (DO) blocks cause issues. If DO is blocked, turn it off. Use a CSP policy.
Win32 app deployment is the best way. It is also the easiest. It helps manage many apps. This is true in Microsoft Intune. You get many good things.
It is flexible.
You can change it.
It handles errors well. Use this guide. It has steps. It will make your Intune deployment better. You will manage Intune better. Learn Win32 app packaging. It helps you deploy apps easily. It gives you control.
FAQ
Why are Win32 apps best for Intune?
Win32 apps are flexible. They handle hard installs. They use custom scripts. They work with many app types. You control app installs.
Do I always need the IntuneWinAppUtil tool?
Yes, you need IntuneWinAppUtil. It packages your app files. It makes the .intunewin format. Intune needs this file type. This is for Win32 app deployments.
How do I fix a failed Win32 app deployment?
First, check the IntuneManagementExtension.log file. It is on the device. Find it at C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension\Logs. This log shows errors. It helps you find the problem.
Can I update apps with Win32 app deployment?
Yes, you can update apps. Use the supersedence feature. It is in Intune. Pick the old package. Then, replace it. Use your new Win32 app. This updates software well.