More people are using AI, with adoption rates between 72% and 78% in 2024, indicating rapid technological advancement. Many users are concerned about their personal information and how Microsoft ensures data protection when they utilize AI tools. Microsoft acknowledges these concerns. This blog details Microsoft’s robust strategy, demonstrating how they maintain privacy and security. This reassures users and offers practical advice. Microsoft aims to build user trust by being transparent about its AI practices and guaranteeing the safety of user data. We will explain how Microsoft safeguards your data and enhances overall security for everyone.
Key Takeaways
Microsoft has strict rules. These rules protect your data. This happens when it makes AI tools. It only gathers necessary data. It uses this data for clear reasons.
Microsoft lets you control your data. You pick what info you share. You also decide how AI uses it.
Microsoft uses good security tools. These tools keep your data safe. This means hiding your data. It also means checking who can see it.
Microsoft obeys privacy laws worldwide. These include GDPR and HIPAA. This makes sure your data is handled right. It also makes sure it is legal.
You can help keep your data safe. Use strong passwords. Learn about safe AI use. This team effort makes AI safer for all.
Microsoft’s Core Principles for AI Privacy
Microsoft builds its AI features. It uses strong data privacy rules. These rules guide AI development. They ensure data protection. Microsoft approves AI tools. These tools use public, confidential, and highly confidential data.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Microsoft uses data minimization. AI systems only collect needed data. They use it for their purpose. Microsoft limits purpose strictly. It stops AI services from causing harm. It stops illegal uses. It stops uses against its Code of Conduct. For example, services cannot make bad content. They cannot make money from it. Restrictions also stop AI for big decisions. This is without human checks. It stops tricking users. It stops using weaknesses. Microsoft also forbids social scoring. It stops profiling that causes unfairness. It stops sorting people by body data. This is for private things. It generally does not allow guessing private things. It does not allow guessing feelings. This is without user permission. This keeps user data ethical. It keeps it focused.
Transparency and Explainability
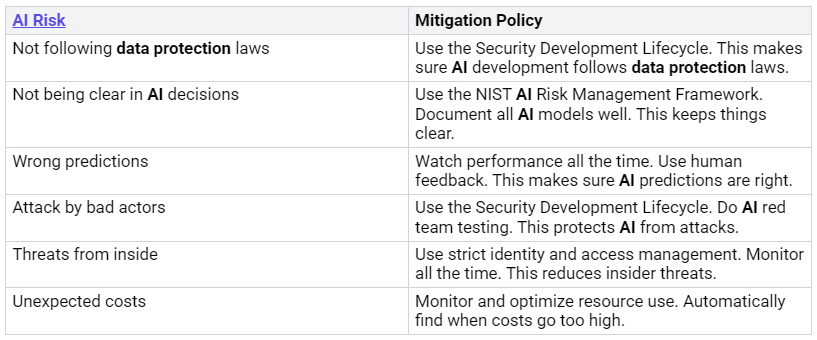
Microsoft wants users to know. They should know how AI systems work. It gives tools and papers. These explain AI decisions. The Azure Machine Learning Responsible AI dashboard helps. It shows how models predict things. This includes overall explanations. It shows what affects the model. It also has local explanations. It shows why a loan was approved. The dashboard checks fairness. It looks at model explanations. This is for certain data groups. Microsoft also has Azure AI Foundry. This platform has ways to measure. It checks the quality of AI content. It checks its safety. These tools help users. They help understand AI decisions. They build trust in AI.
User Control and Consent
Giving users control is key. They control their data. Microsoft gives many choices. These manage data and user wishes. Dynamics 365 Customer Insights – Journeys has preference centers. These let customers choose. They choose how they get messages. They choose how they are contacted. Microsoft Priva Consent Management helps too. It makes managing agreed personal data easy. It has custom consent models. It has a central way to share them. Microsoft Consent Mode changes how tags work. This is based on visitor consent. This makes sure tags do not collect data. This is without clear user permission. These tools help users. They manage their privacy settings well.
Responsible AI Development
Microsoft’s Responsible AI program has six rules. These are fairness, being open to all, being safe, being clear, privacy, and being accountable. Microsoft says ‘fairness’ means giving fair code ideas. This promise makes sure AI treats everyone fairly. Microsoft also has a strong internal system. This includes a Responsible AI Council. It also has an Office of Responsible AI (ORA). The ORA gives advice on rules. It gives advice on how to manage. It made the Microsoft Responsible AI Standard. A required internal tool guides developers. It helps them check AI. This puts responsible AI into making software. Teams register new AI systems. This is during the design part. They give important information to check. A full check before release happens. This makes sure the AI is ready. This process writes down data use. It writes down possible harms. It writes down ways to fix them. This promise makes sure all AI is safe. It makes sure it is made ethically.
Technical Safeguards for Data Security
Microsoft uses strong technical safeguards. These protect data in its AI features. These steps keep user information very secure. They maintain data protection across all services.
Encryption and Access Controls
Microsoft uses full encryption. It also has strict access controls. These keep data safe. Azure OpenAI services encrypt data automatically. This includes training data. It also includes fine-tuned models. They use FIPS 140-2 compliant 256-bit AES encryption. This process is clear. Microsoft handles encryption and access. This keeps data security. Users do not need to do anything. Azure AI Content Safety also encrypts data. It uses FIPS 140-2 compliant 256-bit AES encryption. This automatic process makes data security default.
Microsoft 365 uses different tech for data in transit. TLS encrypts files between users. This includes Microsoft 365 documents. Email in transit uses Microsoft Purview Message Encryption. It uses Azure Rights Management, S/MIME, and TLS. Chats, messages, and files in Microsoft Teams use TLS and MTLS. This is for instant messages. Secure RTP (SRTP) encrypts media traffic. Teams also uses FIPS compliant algorithms. This is for encryption key exchanges.
Microsoft’s AI platforms control access. They use several methods. They protect private information. Microsoft Entra ID replaces API keys. This gives central identity management. It boosts security for services. These include Azure AI Foundry and Azure OpenAI. Microsoft Entra Agent ID keeps good records. It tracks AI agent identities. This enforces rules. It stops ‘shadow AI‘. Multifactor Authentication (MFA) adds a key security layer. Privileged Access also helps. This fights against stolen login info. Conditional Access Policies give smart security. They use risk signs. This stops unwanted access. Least Privilege Access Principles lower security risk. They give only needed permissions. They use Azure role-based access control (RBAC). Microsoft Purview makes access controls better. It improves data protection. It uses Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies. These policies stop AI apps. They stop apps like Microsoft 365 Copilot. They stop them from using private content. This is based on sensitivity labels.
Microsoft 365 Copilot’s permissions stop data leaks. It includes:
Microsoft Purview sensitivity labels and encryption: Copilot works with these. They add more protection. When a labeled file opens, the label shows. Its content markings show too. If encryption is on, the user needs rights. They need EXTRACT and VIEW rights. This lets Copilot summarize the data. New content from Copilot gets the highest label. It gets its protection settings too.
SharePoint oversharing controls: Features like Restricted SharePoint Search exist. They limit search. They limit Copilot experiences. This is for certain SharePoint sites. This is a temporary step. It helps review permissions. It helps apply them correctly.
The permissions in your Microsoft 365 tenant help. They stop data from leaking by accident. This is between users, groups, and tenants. Microsoft 365 Copilot only shows data each person can see. It uses the same controls for data access. These are used in other Microsoft 365 services. Semantic Index respects user access limits. This means the grounding process only uses content. It uses content the current user can access.
Secure Development Lifecycle
Microsoft builds security into AI development. This happens at every step. It uses a Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL). The SDL makes sure security and privacy are in AI systems. They are built in from the start. Microsoft uses a required internal tool. This tool guides developers. It helps them check AI. This puts responsible AI into making software. Teams register new AI systems. This is during the design part. They give important info to check. A full check happens before release. This makes sure the AI is ready. This process writes down data use. It writes down possible harms. It also lists ways to fix them. This promise makes sure all AI is safe. It makes sure it is made ethically. Microsoft also uses the Security Development Lifecycle. This ensures AI development follows data protection laws.
Data Residency and Governance
Microsoft has strict data residency rules. It also has governance policies. These rules keep user data in certain areas. This meets legal needs. Microsoft 365 Copilot’s permissions model builds on tenant isolation. This keeps each organization’s data separate. This is in Microsoft’s shared system. It stops unwanted access. This is across different companies. Zero Trust means Copilot checks every request. It checks every user, device, and resource. It treats each as possibly bad. This lowers the risk of unwanted data access. Full encryption protects data. It protects data stored and moving. Data residency rules make sure Copilot follows Microsoft’s rules. It keeps data in chosen areas.
Microsoft’s AI platforms have strict data rules. They also have access controls. They set data boundaries. This clearly separates information. It is based on user permissions. It is also based on app scope. This stops private data from being seen. They separate datasets. This makes sure each AI job works in its own data space. It uses separate Azure storage. It uses separate databases or data lakes. This stops mixing of data. They set up Role-Based Data Access Controls. This uses Azure RBAC policies. It matches data access to user roles. This reduces privilege abuse. It reduces unwanted data exposure. Microsoft Purview helps find data. It helps classify data. It helps manage compliance for AI systems. It watches data history. It classifies private info. It enforces rules. Rules also aim to make data better. This includes cleaning data. It includes standardizing data. They improve metadata and documents. This creates strong data rules. It uses tools like Microsoft Purview Data Lifecycle Management. This helps enforce policies.
AI-Powered Security Tools
Microsoft offers advanced AI security tools. These tools protect its AI systems. They also protect customer data. These tools find threats faster. They find them more accurately. They use machine learning. This analyzes huge amounts of data. They spot odd things. They find possible threats right away. They learn from patterns. They get better over time. A main benefit is automation. Actions can start when a threat is found. For example, blocking bad emails. Or isolating infected devices. These tools work well with Microsoft 365. They give constant security. This is across Teams, SharePoint, and OneDrive.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud uses AI. It analyzes attack paths. It shows possible attack routes. It finds weak spots in cloud systems. This helps with proactive security. Microsoft Sentinel is a cloud SIEM solution. It uses AI to gather security data. It analyzes and responds to it. It puts data in one place. This helps find threats. It helps with automated responses. Microsoft Purview uses AI. This is for advanced data protection. It covers organized and unorganized data. It automatically finds strange access. It finds possible data leaks. It sends alerts right away.
Microsoft’s AI security tools find new threats. They respond to them. Microsoft Security Copilot is an AI assistant. It helps security and IT teams. It manages threats fast. It protects at AI speed. It uses global threat info. It uses best practices. It uses company data. It uses Microsoft and partner tools. It creates custom insights. This helps respond faster. It helps find threats. It is the only security AI product. It mixes a special language model. It has security features. Microsoft’s global threat info helps it. Over 84 trillion daily signals inform it.
Microsoft’s AI security tools also protect AI itself. They find new AI threats. Microsoft Defender extends AI cybersecurity management. It covers many models and clouds. This includes Google VertexAI. It covers all models in Azure AI Foundry. It shows AI cybersecurity posture. This is from code to running. It covers Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, and Google Cloud. New detection and protection for AI threats will be in Microsoft Defender. This will cover OWASP risks. Examples are indirect prompt attacks. Also, sensitive data exposure. These protect custom AI apps. Microsoft Entra internet access has an AI web filter. This controls access. It stops ‘shadow AI‘ risks. It manages access to different AI apps. Microsoft Purview browser data loss prevention (DLP) stops private data. It stops it from being typed into AI apps. This helps stop cyber attacks and breaches. These tools use lots of threat info. They process 84 trillion signals daily. This keeps up with growing cybersecurity threats.
AI Risk Mitigation Policies
Ensuring GDPR Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
Microsoft makes sure its AI tools follow global privacy rules. This is a key part of its AI plan. Microsoft’s Responsible AI Standard (RAI Standard) helps with GDPR. It sets rules for making AI systems. It also sets rules for managing risks. The RAI Standard lists goals for Microsoft’s AI principles. It includes an Impact Assessment. Teams write down results for each goal. For Privacy & Security, it means following Microsoft’s privacy rules. It also includes AI-specific advice. Microsoft keeps data and models safe. It protects people’s right to privacy.
Global Privacy Regulation Compliance
Microsoft’s Product Terms explain the rules. They cover using Microsoft Online Services. This includes AI features like Microsoft 365 Copilot. These terms are key for following rules. They are also key for contracts. Microsoft handles customer data. It follows the Product Terms strictly. It also follows the Data Protection Addendum (DPA). Data is only used to give services. Microsoft never uses it to train models. This is unless it has clear permission. Customers must follow Microsoft’s Acceptable Use Policy. This policy stops bad use of AI features. It stops getting around safety filters. It stops changing metaprompts. The terms show who does what. Microsoft handles the tech. It handles model operations. It handles safety systems for Copilot. Customers must use it right. They must control access. They must teach users. The terms list all covered services. They show how they meet Microsoft’s promises. This includes privacy and security. The Product Terms help users see how Microsoft works. This includes AI services. Microsoft updates these terms often. This is for new tech and rules. It also includes the Responsible AI Standard (RAIS).
Microsoft takes steps for CCPA and HIPAA. This is for its AI services. It offers a Business Associate Agreement (BAA). This is through the DPA. This BAA is vital for HIPAA. It helps when handling health info (PHI). Microsoft lists some Azure AI services. These are good for HIPAA with PHI. They include Azure OpenAI Service. Many Azure Cognitive Services are included. Text Analytics, LUIS, Speech Services, and Translator are examples. Azure Machine Learning and Azure Bot Services are too. Customers must set up their systems. They must meet security rules. They must use HIPAA settings.
Microsoft finds compliance risks. It manages problems in its AI tools. It checks input data. It cleans it. It limits AI’s access to sensitive info. It checks who people are. It makes secure business processes. Microsoft stresses good monitoring. It stresses checking and watching. This makes sure AI works safely. It works responsibly. It promotes using commercial AI tools. These have built-in safety. Examples are bias checks. Also, input cleaning. Microsoft matches AI rules to new laws. Examples are DORA, GDPR, HIPAA. It keeps good AI records. It uses AI tools to check rules. It checks AI decisions for fairness. It checks for openness.
Microsoft Purview tools help find risks. They help manage them. Microsoft Purview Insider Risk Management finds internal risks. It investigates them. It lessens them. Examples are stealing ideas. Also, data leaks. It uses machine learning. It uses info from Microsoft 365. It has privacy controls. It has a ‘Risky AI usage policy template’. This finds prompt attacks. It finds access to protected stuff. Microsoft Purview Communication Compliance finds rule breaks. It manages them. This covers communication. It covers AI app prompts and replies. It uses fake names. It uses role-based access. This finds bad communication. It fixes it. Microsoft Purview eDiscovery finds electronic info. It delivers it for legal cases. It searches content in Microsoft 365. It can search user prompts. It can search replies for AI apps. These are in mailboxes. This allows exporting this data. These tools help find risks. They help check them. They find and reduce risks. This includes too much data. It includes too much exposure. It includes bad communication. They respond to problems fast. They find data for problems. This helps with quick responses. They follow rules. They follow company policies. They protect privacy. They protect sensitive data. This ensures compliance. They make things better with AI. They use automation. They check large amounts of data. They prioritize actions. They reduce risk with AI.
Industry-Specific Standards
Microsoft follows its ‘Responsible AI Standard’. This is for its AI services. This standard lists rules. It shows how Microsoft makes AI systems. It guides internal teams. It turns AI principles into real practices. Principles are fairness, reliability, safety, privacy, security, openness, and being accountable. Microsoft’s Data Protection Requirements (DPR) now have AI rules. Version 10 has 18 new rules. These are in ‘Section K’. These rules apply to all suppliers. They apply to those using AI systems. They cover how AI is used. They cover technical controls. They include new contract terms. They require someone to watch AI systems. They include new training. They include problem response. They set clear lines for risk checks. They set lines for management. They need clear info about use. They need health checks. They need explanations for decisions.
Certifications and Attestations
Microsoft accepts outside frameworks. This shows suppliers follow its DPR. This is for security and privacy. These frameworks include ISO 27001 for security. ISO 27701 is for privacy. HITRUST certification is for security and privacy. The HITRUST certification is only for HIPAA companies. It is for U.S. healthcare providers. Microsoft 365 Copilot meets top global rules. This includes SOC 2 Type II. It includes ISO 27001. It includes FedRAMP. It follows GDPR and HIPAA.
Best Practices for Secure AI Use
Companies must use good ways. This makes AI safe. It keeps privacy and security strong. This is for all user data. Microsoft helps with this.
Strong Authentication and Authorization
Microsoft says to use strong ways to log in. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a top way. It stops bad users. It asks for more than one check. Microsoft Entra ID has many MFA choices. Conditional Access lets you set special security rules. These rules check things first. They check before letting a user in. They check who the user is. They check the device’s health. Companies should give only needed access. This is called Least Privilege. Users get only what they need. This lowers risks. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) works with this. It helps manage security risks. MFA that stops phishing is best. This is like logging in without a password. It makes security better.
Data Governance and Classification
Companies must manage data well. They must sort data. This is for AI-processed data. First, sort the data. Use labels to mark sensitive data. Do this before AI uses it. Tools can sort automatically. They find personal info. This protects privacy. Second, control data. Set who can access it. Use less data when possible. This is for these tasks. Safeguards should clean sensitive data. They should remove it from logs. They should stop bad requests. This protects privacy. Third, watch data. Track where data comes from. Watch how models perform. Look for problems. Do this all the time. Make ways for users to report bad outputs. This keeps privacy safe. Fourth, make things better. Change processes based on checks. Change them based on user ideas. Change them for new rules. Managing data needs constant work. This is for privacy.
Employee Training and Guidelines
Companies must teach everyone important. They need to know how AI works. This is more than just ads. Make rules for safe AI use. Do this in Microsoft 365. These rules meet cybersecurity needs. Teach employees about right and wrong. Teach them about privacy laws. Teach them to use AI wisely. This protects privacy. Training should cover company secrets. It should balance getting work done. It should balance keeping data safe. Employees need help with handling data safely. They need it for good choices. They need it to follow laws. This builds a culture of good ethics. It makes sure laws are followed. This also makes privacy better.
Continuous Monitoring and Audits
Watching AI risk all the time is key. Models change and learn. They see new data. Look for strange things. Look for them in inputs and outputs. Also, look for strange model behavior. This includes changes or bad data. Track important performance and risk signs. These include how accurate it is. They include unfairness. They also include made-up answers. They include attempts to misuse it. Do practice runs for problems often. These cover model hacks. They cover data leaks. They cover attempts to trick AI. Apply zero-trust rules to all access. This includes users, services, and agents. Checking all the time is key for security. Regular IT security checks find problems early. Microsoft Defender makes AI cybersecurity management better. It works for many models and clouds. This helps keep AI cybersecurity strong. This keeps privacy and security safe.
Microsoft keeps its promise. It protects user privacy. It secures AI features. The company uses key rules. It has strong tech safeguards. It follows strict compliance. These steps protect user data. Microsoft uses advanced encryption. It uses access controls. This makes data private. It boosts overall data security. This approach keeps user data safe.
A secure AI environment needs teamwork. Microsoft and users must share this. User actions affect data security. They also affect privacy. Microsoft always improves its security. It changes for new AI threats. It pushes for responsible AI. This keeps user data private. It upholds strong security. Microsoft leads this work.
FAQ
How does Microsoft keep my data safe in AI?
Microsoft uses strong ways to hide your data. It controls who can see it. It only uses data it needs. This keeps your data safe.
Can I manage my data with Microsoft AI?
Yes, you can. Microsoft lets you control your data. You can choose what you share. This means your choices are followed.
Does Microsoft use my data to teach its AI?
No, it does not. Microsoft will not use your data. It needs your clear permission first. This keeps your data private.
How does Microsoft make sure AI is secure?
The company builds security into AI. It finds threats quickly. It fixes problems fast. This protects AI and your data.