Non-human identities are quickly becoming very important in identity governance. In cloud environments, there are 45 non-human identities for every human one. Some companies report ratios from 10:1 to even 92:1. This rise in non-human access comes from more automation, cloud computing, and AI technologies. As organizations use these new tools, they pay more attention to securing non-human identities. In fact, 42% of security experts now focus on protecting non-human access more than human users.
Key Takeaways
Non-human identities (NHIs) are very important today. There are 45 NHIs for every human identity. Managing these identities well improves security and how things work.
If NHIs are not managed, they can cause big problems. This includes unauthorized access and insider threats. Organizations need strong rules to reduce these risks.
Using a Zero Trust approach makes sure every access request is checked. This improves security for both human and non-human identities.
Workload identities make it easier to manage access for apps and services. This improves security and compliance while making it harder for attacks.
Regular reviews of permissions and using automation can help keep NHIs safe. This ensures compliance and lowers security risks.
Non-Human Identities
Define non-human identities and their relevance in identity governance
Non-human identities (NHIs) are digital things that do tasks without people. They include API keys, service accounts, and automation bots. NHIs are very important in identity governance. They help companies control who can access resources. This makes sure only the right entities can do certain actions. By defining and managing these identities, you can make security better and make operations easier.
Discuss the significance of NHIs in modern organizations
In today’s digital world, NHIs are key for working well. Companies depend on them for many tasks, like automating work and connecting services. Here are some common types of non-human identities you might see:
API Keys
Cloud Services
Containers and Images
DevOps Tools
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Bots
Service Accounts
Software Supply Chain
SaaS-to-SaaS Integrations
These identities help systems and applications talk to each other. They also allow for faster service deployment, which is important for staying competitive.
Highlight the risks associated with unmanaged NHIs
But unmanaged NHIs can create big risks. Without proper control, these identities can cause security problems. For example, orphaned accounts can be targets for insider threats. Bad ownership can give too many privileges, making it easier for attackers to take advantage of weaknesses. Also, too many alerts can confuse your security teams, making it hard to find real threats.
To reduce these risks, companies should work on securing non-human identities. By using good identity governance practices, you can improve visibility and control over these identities. This not only lowers risks but also helps with compliance and makes operations better.
Challenges of Non-Human Access
Explore the complexities and vulnerabilities of managing non-human access
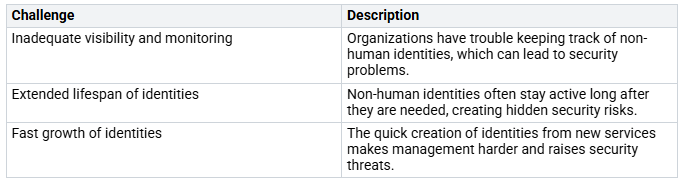
Managing non-human access has special challenges. Non-human identities (NHIs) often stay active long after they are needed. This can create security risks because these identities might not be watched closely. New services create many identities, making management harder. Traditional identity and access management (IAM) tools mainly focus on human users and ignore machine identities.
Here are some main technical challenges organizations face when managing non-human access:
Discuss the attack surface and governance gaps
The attack surface from non-human identities is very large. In cloud environments, there can be about 10,000 non-human connections for every 1,000 users. This wide use of NHIs makes them a big risk. Managing so many NHIs by hand is almost impossible.
Common governance gaps that attackers take advantage of include:
Not properly removing non-human identities can allow unauthorized access.
Secret leakage happens when sensitive information is not well protected.
Overprivileged non-human identities create weaknesses that attackers can use.
These gaps show the need for strong governance practices. Without proper control, NHIs can gain too many permissions over time, raising the risk of being exploited.
Address compliance issues related to non-human identities
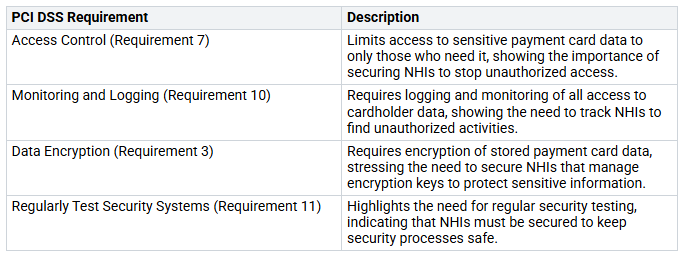
Compliance rules are increasingly stressing the need to manage non-human identities. For example, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) has several rules that relate directly to NHIs:
Many organizations find it hard to meet these compliance rules. They often do not have a clear view or list of active NHIs. Who owns these identities is often unclear. Managing credentials is another area where organizations struggle, as many programmatic secrets are not changed or expired as needed by standards like PCI DSS.
By tackling these challenges, you can improve identity security and make sure you follow important regulations.
Zero Trust and Identity Governance
Explain the Zero Trust approach in the context of identity governance
The Zero Trust approach changes how you view identity governance. Instead of thinking users inside your network are safe, Zero Trust says you must check every access request. This model highlights that no part, person, method, or process should be trusted automatically. You need to focus on the identity behind each account because every attack connects to a user account. By using this way of thinking, you can improve your identity security and lower the chance of unauthorized access.
Discuss the principles of Zero Trust
Zero Trust works on several important principles that guide your security plan:
Don’t Trust Anything: Always check the identity and context of every access request.
Place User Identities at the Forefront: Focus on the identity behind the account for strong security.
Guarantee the Highest Possible Level of Security: Use the best security measures to stop costly breaches.
Do Not Rely on the Traditional Firewall Boundary with VPN: Basic security measures are just the start; you need more complete actions.
Provide Practical and Secure Access to Resources: Balance security with usability so users can do their tasks well.
These principles help you build a security system that always checks identities and adjusts to changes.
Highlight how Zero Trust applies to non-human identities
Zero Trust is very important for managing non-human identities (NHIs). Here are some ways to use Zero Trust ideas for NHIs:
Define Zero Trust Policies: Treat NHIs like important accounts, making sure they follow strict access rules.
Leverage Automation: Use automated systems to manage NHIs well, lowering the chance of human mistakes.
Monitor Activity: Always check logs to find unusual behavior related to NHIs.
Using these strategies helps you keep control over NHIs, making sure they work within set security rules. Also, think about these main ideas for managing NHIs:
Least Privilege: Limit machine credentials to only what they need to work.
Short-Lived Credentials: Use tokens that expire quickly to lower risk.
Continuous Monitoring: Regularly check and track actions to find problems.
Automation: Use automated tools for credential management to handle many NHIs.
By using Zero Trust ideas throughout the machine identity lifecycle, you can see NHIs as key parts of your identity management program. This way makes sure that access decisions consider the context, checking where the request comes from and other factors before allowing access.
Workload Identity Solutions
Introduce workload identities as a solution for managing non-human access
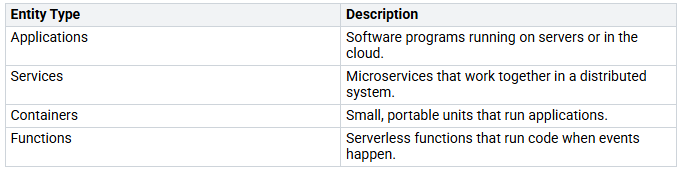
Workload identities are important for managing non-human access. They help applications, services, containers, and serverless functions to verify and allow their actions. By using workload identities, you can control and watch over access to resources like databases, APIs, and storage services. This method improves security and compliance by giving each workload a unique identity.
Here’s a list of the types of entities that benefit from workload identities:
Discuss the benefits of adopting workload identities
Using workload identities has many clear benefits for organizations. Here are some key advantages:
Reduce attack surface: You can find and remove unused accounts or privileges that hackers might use.
Improve incident response: Real-time alerts linked to identity management help you respond faster.
Boost productivity: Cut down on login problems that slow down workers.
Reduce frustration: Provide secure access without too many obstacles, like extra MFA prompts.
Audit preparedness: Quickly show proof of policy enforcement during checks.
Risk reduction: Compliance often helps with security, lowering legal and reputation risks.
Faster onboarding: Help new employees be productive right away.
Immediate offboarding: Quickly remove access for leaving employees to close security gaps.
Lower IT workload: Decrease help desk requests with self-service tools and automation.
These benefits show how workload identities make both security and operations better for non-human access.
Explain lifecycle management and conditional access enforcement
Good lifecycle management of non-human identities is key for reducing risks and improving compliance. You should set up a governance process to define how to handle these identities. Regularly check usage to ensure it follows the defined permissions. Change credentials often to boost security and set clear expiration dates for identities and credentials. Have a formal process to remove identities from active use.
Conditional access enforcement is very important for managing non-human identities in cloud settings. It uses unique identities and short-lived tokens, along with policy engines that provide context-aware access controls. These engines check the identity of workloads and their operational context, allowing you to apply least privileged access dynamically. For example, a workload may only access sensitive data if it meets certain conditions, like being in a production environment and passing security checks.
By using these practices, you can make sure your identity security management stays strong and effective, lowering the risks linked to unmanaged non-human identities.
Enhancing Identity Security
Provide strategies for improving identity security for non-human identities
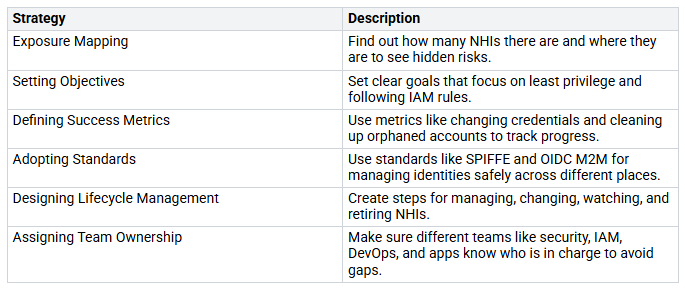
To make identity security better for non-human identities (NHIs), you can use some smart strategies. First, start with exposure mapping. This helps you find out how many NHIs there are and where they are located. This step helps you see any hidden risks. Next, set clear goals that focus on least privilege and following identity management rules. You should also create success metrics, like how often you change credentials and clean up orphaned accounts. This way, you can track your progress and fix any problems.
Here’s a summary of key strategies:
Discuss entitlement reviews and audit trails
Entitlement reviews are very important for lowering risks with NHIs. They make sure that NHIs have the right permissions based on the least privilege rule. Regular reviews help find and fix NHIs that have too many permissions, which lowers the chance of security problems. A simple review process can help a lot by checking if an NHI is still needed.
Audit trails help with compliance by making sure you meet rules. They keep track of what NHIs do in identity and access management systems. The unique identifier, called the Secret, is key for keeping security strong. By keeping detailed logs, you can see who accessed what and find any unauthorized actions.
Highlight the role of automation and AI in identity management
Automation and AI make managing NHIs much better. Automation helps by doing many tasks without needing constant human help. It allows you to manage many unique identities as applications change. These identities help provide secure and repeatable access, following the least privilege rule and lowering security risks.
AI improves visibility, automation, and security for both human and non-human identities. Smart monitoring and spotting unusual activities happen through ongoing checks of API interactions and service accounts. AI-driven access governance automates role mining and compliance checks, which cuts down on manual work. Managing the lifecycle of NHIs gets better with automation for adding and removing identities, which reduces human mistakes.
In short, managing non-human identities (NHIs) is very important for your organization’s safety and rules. NHIs are much more common than human identities, with at least 45 NHIs for every human one. This means there are big risks if these identities are not managed well. You should focus on strategies like automated ownership management and lifecycle automation to reduce these risks.
“NHIs are digital identities for applications, services, or devices… often falling outside traditional IAM controls, making them particularly vulnerable when left unmanaged.” — CrowdStrike
By using good governance practices, you can improve visibility and control over NHIs. This helps keep your environment safe and compliant as you deal with the challenges of modern identity management.
FAQ
What are non-human identities?
Non-human identities are digital things like API keys, service accounts, and automation bots. They do tasks without people, which makes them very important for today’s work.
How does zero trust apply to non-human identities?
Zero trust means checking every access request, even from non-human identities. This way, you look at the context and identity behind each request to make security better.
Why is lifecycle management important for NHIs?
Lifecycle management helps you keep track of, manage, and remove non-human identities properly. This process lowers security risks and helps follow rules.
What is conditional access?
Conditional access is a security method that gives access based on certain conditions. It makes sure non-human identities can only get to resources when they meet set rules.
How can I implement practical workload IAM?
You can use practical workload IAM by giving unique identities to applications and services. This method improves security and makes it easier to manage service-to-service communication.