Reliable Power Apps deployments are crucial for maintaining smooth business operations and ensuring user satisfaction. By implementing good practices, you can streamline the deployment process, allowing for faster changes with fewer mistakes. Utilizing DevOps and ALM practices enhances the reliability of your app deployments. Through automation and consistent strategies, you can minimize human errors, ensuring safe and secure deployments. These methods also foster improved collaboration among teams, significantly elevating the quality of the Reliable Power Apps you deliver.
Key Takeaways
Use Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) to make your Power Apps deployments easier and safer.
Use DevOps methods to improve teamwork and automate deployment tasks. This helps to lower mistakes.
Use version control methods to handle app changes well and make sure deployments go smoothly.
Check your Power Apps often to find problems early and keep a good user experience.
Work on ways to improve all the time. This keeps your deployments effective and ready for business needs.
ALM Importance for Reliable Power Apps
Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) is very important for reliable Power Apps deployments. ALM includes the steps and tools that handle the whole life of an application. This starts from the first development to deployment and maintenance. When you use a good ALM plan, you can lower risks that come with manual deployments.
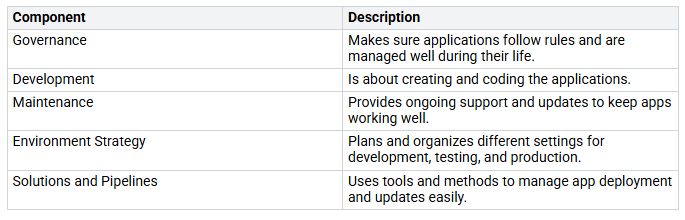
Key ALM Components
Knowing the main parts of ALM helps you build a strong base for your Power Apps projects. Here are the key parts:
Each part helps make your deployments more reliable. For example, governance makes sure your app development follows rules and regulations. This helps with compliance and shows how work is going. Also, having separate environments for development, testing, and production stops problems between workstreams, which lowers the chance of mistakes.
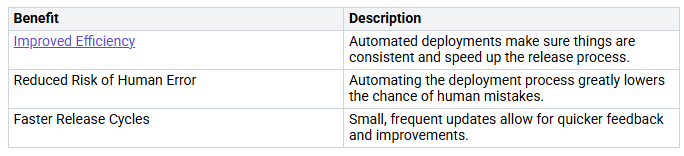
Benefits of ALM in Power Platform Success
Using ALM in your Power Platform projects has many benefits. Here are some clear advantages you can see:
With a good ALM plan, you can make your deployment process smoother. This leads to faster release cycles and better efficiency in software development. Plus, automating tasks reduces the workload for administrators. This lets them focus on more important tasks.
Manual deployments can be risky, like causing security issues and data leaks. For example, using SharePoint as a data source can make managing permissions tricky. This can lead to app failures and unauthorized data access. By using ALM practices, you can reduce these risks and make your Power Apps deployments more reliable.
Best Practices for DevOps Integration
Bringing DevOps into your Power Apps deployments can greatly improve how you develop and deploy. By focusing on teamwork and version control, you can make your processes smoother and more efficient.
Collaboration Strategies
Good teamwork is key for successful Power Apps deployments. Here are some ways to boost collaboration:
Define Clear Purposes: Set clear roles for development, testing, and production. This helps stop unwanted changes and keeps things compliant.
Engage Multidisciplinary Teams: Work with both business experts and developers. Fusion teams, which mix domain experts and IT staff, help connect business needs with tech solutions.
Regular Monitoring: Watch over your environments closely. Regular checks ensure reliability and scalability, helping you fix problems before they grow.
Upskill In-House Teams: Provide training for your teams. This keeps your apps in line with changing needs and lowers mistakes during deployment.
By using these strategies, you can speed up deployments and cut down on errors. Better teamwork leads to quicker updates and improved quality checks, making the deployment process more reliable.
Version Control Techniques
Version control is very important for managing your Power Apps source code and settings. Here are some useful techniques:
Built-in Version Control: Use Power Apps Studio’s basic versioning tools. This helps you track and restore old versions of your apps easily.
Source Control Systems: Save your apps as .msapp or YAML files. Using these with Git helps team members work together and keep track of changes.
Branching and Merging: Use branching methods to handle different features or versions. This lets developers work separately, reducing conflicts.
Automated Deployment and CI/CD: Use tools like Azure DevOps for automatic processes. Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) cut down on errors and keep deployments consistent.
Best Practices: Always back up your work, write down changes, and do team reviews. These steps are key for keeping code quality high and ensuring smooth deployments.
By following these version control techniques, you can make your Power Apps deployments more consistent and reliable. CI/CD pipelines help manage code, improve teamwork, and catch issues early, leading to better quality solutions.
Power Platform Pipelines for Automation
Power Platform pipelines are very important for automating your deployment tasks. They help move solutions through different environments. This makes sure everything is tested and approved without needing manual work. Automation cuts down on mistakes and problems, which improves your application lifecycle management. Here are some main benefits of using pipelines:
Automate boring tasks like exporting and importing solutions.
Remove human errors like missing parts or wrong versions.
Make sure validation and approval happen at each deployment step.
Keep a detailed record of changes and approvals.
Let non-technical users safely move solutions between environments.
Control access to stop unauthorized deployments.
By using these features, you can make your deployments more reliable and efficient.
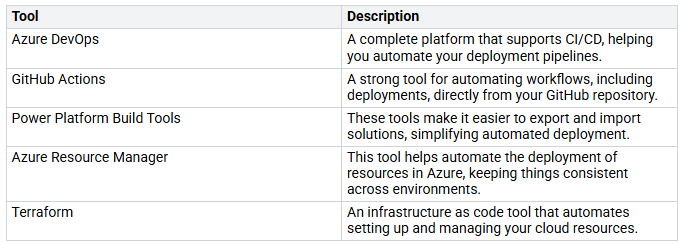
Tools for Automation
Many tools can help you automate deployments well. Here are some popular tools used in Power Platform pipelines:
These tools help you create custom pipelines that meet your needs. They also make your deployment processes more efficient by reducing manual work.
To keep your automated deployments safe and compliant, think about these strategies:
Use a clear Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) plan to lower risks like security issues and non-compliance.
Use solution segmentation to improve security by cutting down system-wide dependencies and enforcing access controls.
Do regression testing to make sure updates do not harm security, functionality, or performance.
By following these practices, you can build a strong system for your automated deployments, making sure they are both secure and efficient.
Testing Strategies for Deployments
Testing is very important in the deployment process of Power Apps. It makes sure your applications work well and meet what users want. By using good testing strategies, you can find problems early and improve the quality of your software. Here are some reasons why testing matters:
Finds and fixes problems early in development
Improves user experience
Cuts down on expensive fixes after deployment
Helps with keeping apps maintained
Lets applications change with business needs
By focusing on testing, you can avoid many problems that come from deploying apps that haven’t been tested.
Types of Testing
Different types of testing are needed to find issues in Power Apps before deployment. Each environment has a special role in the testing process:
Development Environment: This is where you create your app ideas. You can try out features and make changes.
Testing/QA Environment: This environment is key for checking how things work and how users feel. It makes sure everything is ready before deployment.
Production Environment: This is the live space where users use your apps. It needs to stay stable and reliable for a smooth experience.
By using these environments well, you can make sure your deployments succeed and that you give high-quality software to your users.
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Watching your Power Apps after they go live is very important. It helps keep everything running smoothly and users happy. By checking your apps regularly, you can find problems before they get worse. Here are some important things to watch:
Error rates
CPU and memory usage
User experience metrics
These things give you early warnings about possible issues. Keeping an eye on your apps shows you how they perform and how users act. This helps you find and fix problems quickly. Monitoring tools can notify your team right away when something goes wrong. This allows for fast fixes to avoid bigger problems.
Tip: Look at your monitoring data often to see patterns. This can help you make smart choices about improvements and how to use resources.
Improvement Strategies
To make your Power Apps deployment better, think about using these ideas for ongoing improvement:
Continuous Integration: Check code changes with automated tests and compliance checks. This keeps your deployments stable and safe.
Robust Environment Strategy: Handle different stages of development and deployment well. This keeps things consistent across environments.
Utilize CI Pipelines: Automate testing and reporting to get quick feedback on code quality. This lowers the chances of mistakes slipping through.
Integrate Source Control: Link your source control with CI pipelines for real-time updates on pull requests and build statuses. This encourages teamwork and openness.
Quality Checks: Do careful checks on custom code to keep standards and security high. This step is key for making sure your apps are reliable.
Block Failed Deployments: If tests do not pass, stop the deployment process. This pushes your team to look at issues and improve the code before moving on.
Companies that use these strategies often see big improvements. For example, a global automotive finance company set up a structured Power App for idea submissions. This boosted employee involvement and created a clear process with good tracking and audit trails. As a result, they saw a big rise in idea submissions, showing how effective continuous improvement can be.
By focusing on monitoring and continuous improvement, you can make sure your Power Apps deployments are reliable, scalable, and efficient.
In conclusion, using DevOps and ALM is very important for reliable Power Apps deployments. When you use these practices, you can improve teamwork and make your deployment process easier. Here are some important points to remember:
Version Control and Teamwork: ALM helps manage different app versions, making tracking and deployment smooth.
Clear Deployment Steps: ALM sets a clear way to move apps through development, testing, and production, which lowers risks.
Control and Safety: ALM controls who can build and deploy apps, keeping things safe and compliant.
Handling Changes and Improvements: ALM makes it easy to update and improve apps, keeping the system stable.
Saving Time and Money: A good ALM plan automates boring tasks, letting teams focus on new ideas.
By using these strategies, you can make sure your Power Apps stay reliable and meet business needs effectively.
FAQ
What is ALM in Power Apps?
ALM means Application Lifecycle Management. It is about managing your Power Apps from start to finish. This includes development, deployment, and maintenance. ALM helps keep your app deployments consistent and reliable.
Why should I use DevOps with Power Apps?
Using DevOps with Power Apps improves teamwork and automates how you deploy apps. This combination lowers human mistakes, speeds up release times, and makes sure your apps meet business needs well.
How can I automate my Power Apps deployments?
You can automate your deployments by using tools like Azure DevOps or GitHub Actions. These tools help you create CI/CD pipelines. This makes the deployment process easier and reduces manual work.
What types of testing should I perform before deployment?
You should do unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing. These tests find problems early. They make sure your apps work correctly and meet user needs before going live.
How can I monitor my Power Apps after deployment?
You can monitor your Power Apps with analytics tools. These tools track performance, error rates, and how users interact with your apps. Regular monitoring helps you spot and fix issues quickly, ensuring a good user experience.