Hybrid Exchange environments are very important in today’s IT systems. They help different systems talk and work together easily. Learning how to use these environments is key for your organization to run well. But, you might face problems when setting them up or managing them. These problems can include mistakes in settings or connection troubles. This blog wants to give you helpful, step-by-step advice to deal with these issues and keep a stable hybrid exchange environment.
Key Takeaways
Hybrid Exchange environments mix local servers with Exchange Online. This helps improve communication and control over data.
To set it up correctly, you need to meet system requirements. You also need to understand licensing rules to avoid problems.
Use the Hybrid Configuration Wizard for an easy setup. Make sure to check for common issues like misconfigurations.
Regular updates and checking things often are important. They help keep a stable and safe hybrid environment.
Follow best practices like directory synchronization and email authentication. These steps help make security and efficiency better.
Overview of Hybrid Exchange Environment
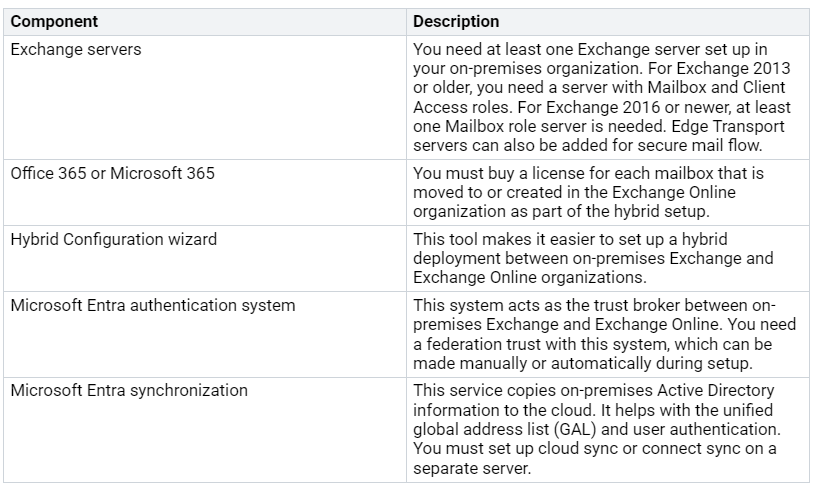
Definition and Components
A hybrid exchange environment mixes on-premises Exchange servers with Exchange Online in Microsoft 365. This setup helps organizations use both systems while keeping control of their data. Here are the main parts of a hybrid exchange environment:
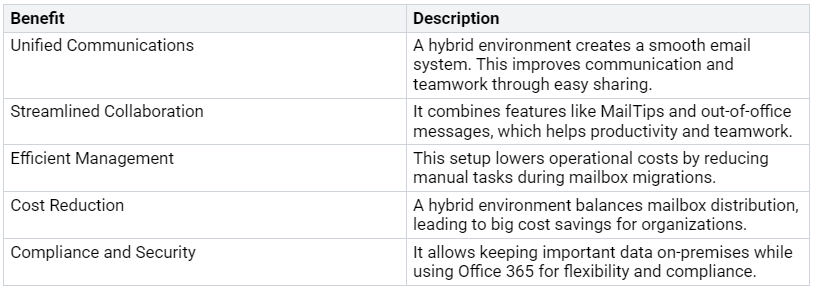
Benefits of Hybrid Exchange
Using a hybrid exchange environment has many benefits for organizations. Here are some key advantages:
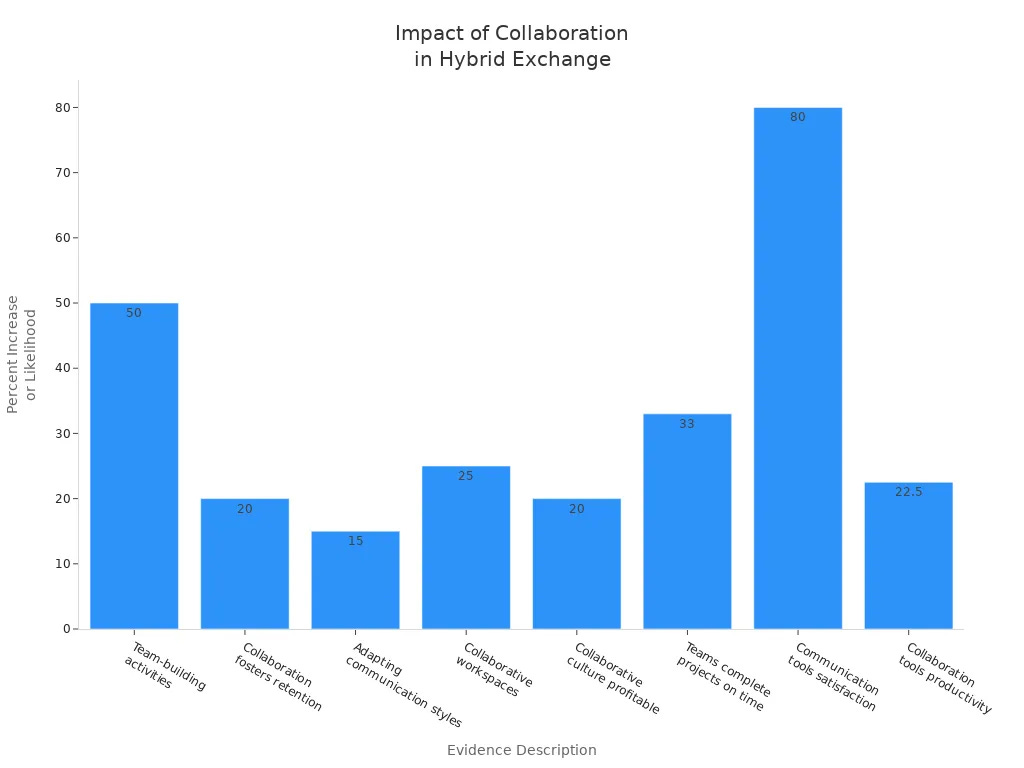
Statistics show that organizations using hybrid exchange environments see better collaboration and communication. For example, companies with a collaborative culture are 20% more likely to make a profit. Also, good communication tools can increase remote worker satisfaction by 80%.
By knowing the parts and benefits of a hybrid exchange environment, you can see how it improves your organization’s communication and teamwork skills.
Prerequisites for Hybrid Exchange Setup
Before you start setting up a hybrid Exchange environment, you need to check some important things. These include system needs and licensing rules.
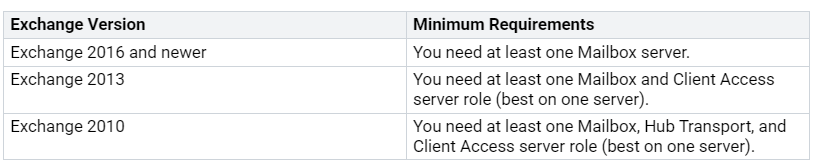
System Requirements
To create a hybrid Exchange environment, your system must meet certain needs. The table below shows the minimum needs based on the version of Exchange you will use:
Make sure your system can handle these needs. This setup helps your on-premises Exchange and Exchange Online work well together.
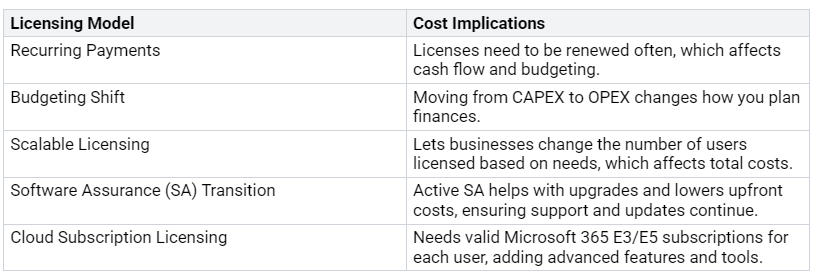
Licensing Considerations
Licensing is also very important for setting up a hybrid Exchange environment. You need to know about the different licensing types and their costs. The table below lists key licensing types:
When moving to Office 365, you might face common licensing issues. For example, all users need an M365 subscription to use Exchange in a hybrid setup. If you are moving from other systems, you may need to set up Exchange Hybrid servers for managing attributes.
By knowing these prerequisites, you can get ready for a successful hybrid Exchange setup.
Building On-Premise Environment
Installing Exchange Server
To start your hybrid Exchange environment, you need to install the Exchange Server first. Here are the steps for a smooth installation:
Open Command Prompt (CMD) as an Administrator.
Run these commands:
Prepare the Schema:
Setup.exe /PS /IAcceptExchangeServerLicenseTerms_DiagnosticDataON
Prepare Active Directory (AD):
Setup.exe /PrepareAD /OrganizationName:”IBT11 LABS” /IAcceptExchangeServerLicenseTerms_DiagnosticDataON
Prepare the Domain:
Setup.exe /PrepareDomain /IAcceptExchangeServerLicenseTerms_DiagnosticDataON
Run the Exchange Server Setup.exe to start installing.
After you install, finish these tasks:
Log in to the Exchange Admin Center (ECP).
Enter your License Key.
Set up Internal and External DNS for Exchange Server 2019.
Create Virtual Directories for Internal and External access.
Use PowerShell to set up the “Autodiscover” Virtual Directory.
Add your public domain to the “Accepted Domains.”
Set up the “Send Connector.”
Import your SSL Certificate or create a CSR request.
Make Mailbox Databases based on your needs.
Configuring Exchange Server Settings
After you install the Exchange Server, you must configure its settings. Good configuration helps your hybrid environment work well. Start by checking your DNS settings. Make sure your internal and external DNS records point to the right Exchange Server.
Next, set up the Autodiscover service. This service helps clients find Exchange services automatically. You can do this using the Exchange Admin Center or PowerShell.
Finally, create your mailbox databases. Make them based on your organization’s needs. Think about storage space and user distribution.
By following these steps, you will build a strong base for your hybrid Exchange environment. This setup will improve communication and teamwork in your organization.
Configuring Azure AD Connect and Mail Flow
Setting Up Azure AD Connect
To set up Azure AD Connect, do these steps:
Open the Azure AD Connect tool and click configure.
Choose customize synchronizing options.
Type in your global Azure AD admin credentials.
Check your Active Directory Forest settings.
Pick Exchange hybrid deployment and click next.
Click configure and do a full import/synchronization.
Make sure you have everything ready. Decide what installation features you need. You can pick either Express Installation or Custom Settings based on your needs. For Custom Settings, choose components, where to install, and sync groups.
Tip: Turn on hybrid deployment with Exchange to keep mailboxes working together. This setup helps you sync public folders and set up password hash synchronization.
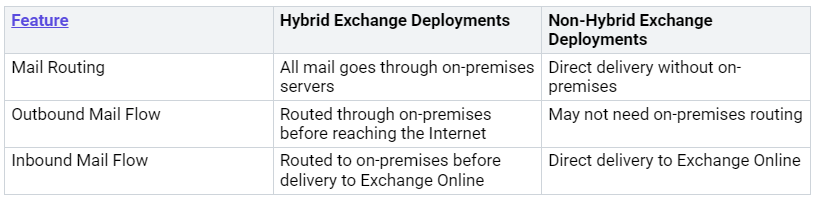
Configuring Mail Flow
Setting up mail flow is very important for a good hybrid Exchange environment. Here are some tips for setting it up:
Point your MX record to Exchange Online Protection (EOP) in Microsoft 365 or Office 365. This helps with spam filtering.
If your MX record goes to EOP, all messages will go through Exchange Online first. This is best if you have more users in Exchange Online.
If rules say you must, you can keep the MX record pointing to your on-premises organization. But, this makes spam filtering less effective.
By following these tips, you can make sure your hybrid Exchange environment works well. Good setup of Azure AD Connect and mail flow will improve communication and teamwork in your organization.
Using the Hybrid Configuration Wizard
Running the Hybrid Configuration Wizard
To set up your hybrid Exchange environment, you must run the Hybrid Configuration Wizard (HCW). Follow these steps for a smooth process:
Check the prerequisites and do topology checks.
Test your account login details.
Make any needed changes for the hybrid setup.
Make sure your Exchange Servers are updated.
Turn on the MRS proxy.
Delete any old versions of the Hybrid Configuration Wizard.
Download the newest version of the Hybrid Configuration Wizard.
Install the Hybrid Configuration Wizard.
Run the Hybrid Configuration Wizard.
Check that the Hybrid Configuration Wizard is installed correctly.
By following these steps, you can set up your hybrid environment well.
Tip: Watch out for common mistakes during this process. Timeout errors often happen because of network problems or wrong firewall settings. Make sure your network is stable and check your firewall rules to allow the right traffic.
Post-Configuration Tasks
After running the Hybrid Configuration Wizard, you need to finish some important tasks to complete your setup:
Update DNS records if you use direct mail flow.
Set up mailbox moves using the New-MoveRequest command in PowerShell or the Exchange Admin Center (EAC).
Train your IT staff to manage mailboxes on both platforms well.
Plan to eventually shut down your on-premises Exchange server, if needed.
To check if your hybrid setup was successful, look at the HCW logs found at %AppData%\Roaming\Microsoft\Exchange Hybrid Configuration. Check for completed tasks and confirm connections to both on-premises and Exchange Online servers.
By finishing these post-configuration tasks, you make sure your hybrid Exchange environment runs smoothly and efficiently.
Migrating Mailboxes and Public Folders
Planning the Migration
Before you start moving mailboxes and public folders, you need to plan well. A good migration plan should have a timeline, a list of tasks, and who is responsible for each task. Here are some important things to think about:
Test thoroughly: Test your hybrid Exchange environment carefully before moving. This helps find any problems.
Communicate with end-users: Keep users updated during the move. This helps manage what they expect and reduces issues.
Monitor the migration process: Watch the migration closely to find and fix any problems quickly.
Make sure user accounts and permissions sync correctly between both environments. Managing mail routing is very important for delivering emails to both on-premises and online mailboxes. Also, handle coexistence management, especially for sharing calendars and working together.
Executing the Migration Process
Once you have a strong plan, you can start the migration process. Follow these steps to make the move smooth:
Download the needed scripts from the Exchange Public Folders Migration Scripts page.
Save the scripts on your computer.
Sync mail-enabled public folder objects to Exchange Online using the PowerShell command given.
Start the migration request by running the required commands in both Exchange 2016 and Exchange Online PowerShell.
To reduce downtime during the move, think about pre-staging mailbox data before the final switch. This helps make the transition faster. Automating the setup of Outlook profiles after the move can also save time and cut down on mistakes, especially for many users.
Be careful of common migration errors. For example, if you find corrupt items or mailboxes causing trouble, try moving the mailbox to different on-premises mailbox databases. If a migration batch gets stuck, clean up old move requests to keep going.
By following these steps and tips, you can successfully move mailboxes and public folders in your hybrid Exchange environment, making it a smooth experience for your users.
Mastering Exchange Hybrid Deployments: Best Practices
Common Issues and Solutions
You might face some common problems when managing your hybrid exchange environment. Knowing these challenges can help you find good solutions. Here are some common issues:
Misunderstandings about Architecture: Many users find hybrid architecture confusing. This confusion can cause wrong settings.
Mailbox Migration Challenges: Moving mailboxes can be hard. You may have problems like losing data or long downtime during the move.
To fix these issues, think about these solutions:
Proactive Monitoring: Regularly check important parts like Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) and Exchange Hybrid. This helps avoid outages and keeps things running smoothly.
Regular Updates and Maintenance: Always keep your systems updated. Renew certificates that are about to expire and apply needed patches to stay reliable.
Also, watch out for security risks like CVE-2025-53786. This risk lets an attacker with admin rights on an on-premises Exchange Server gain more power in the cloud. Microsoft has a Hot Fix to solve this problem, which is important for keeping security in hybrid setups.
Best Practices for Management
To keep your hybrid exchange deployments stable and performing well, follow these best practices:
Entra ID Synchronization: Set up directory synchronization to copy on-premises Active Directory information for mail-enabled objects to the cloud.
Exchange Patch Management: Regularly update and patch your servers. This lowers security risks and ensures reliable email delivery.
Understanding Exchange Hybrid Mail Flow: Use hybrid transport to manage mail flow between on-premises and cloud environments safely.
Email Authentication: Use SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to stop email spoofing and make sure messages are real.
Directory-Based Edge Blocking: Use this feature to block messages sent to wrong recipients. This improves security against phishing attacks.
Enhanced Filtering for Connectors: Keep sender information for better email authentication and filtering accuracy.
Hybrid Modern Authentication: Use this method for better security in user authentication and authorization.
By following these best practices, you can get great results. For example, hybrid deployment migration is the fastest way to move mailbox data to Microsoft 365 or Office 365. Real customer deployments have reached speeds of up to 100 GB/hour. By using best practices, you can keep a steady speed of 30 GB/hour with a specific setup.
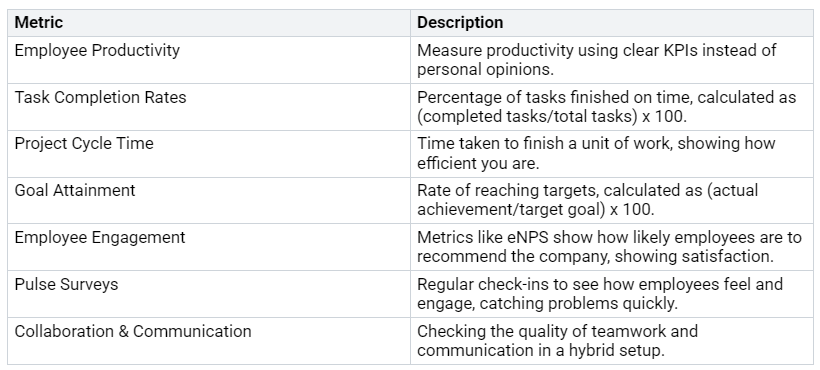
To check how well your management strategies work, think about tracking these metrics:
By focusing on these areas, you can master your hybrid exchange deployments and create a stable, efficient environment for your organization.
Mastering hybrid Exchange environments is very important for good communication and teamwork in your organization. You learned about the parts, benefits, and best ways to manage these environments.
To keep up with new changes, check out these resources:
Evaluating Options for Exchange Server in 2025
By using the helpful steps in this blog, you can improve your hybrid Exchange setup. Keep learning and stay updated in this changing field. Your active approach will help create a more stable and efficient environment.
FAQ
What is a hybrid Exchange environment?
A hybrid Exchange environment mixes on-premises Exchange servers with Exchange Online in Microsoft 365. This setup helps you manage both systems while keeping control of your data.
How do I migrate mailboxes to Exchange Online?
To move mailboxes, plan your migration carefully. Use the Hybrid Configuration Wizard to set up the environment. Then, move mailboxes using PowerShell or the Exchange Admin Center.
What are common issues during migration?
Common problems include losing data, long downtimes, and wrong settings. You can avoid these issues by testing your setup and keeping users informed during the process.
How can I ensure mail flow works correctly?
To make sure mail flow works well, set your MX records to point to Exchange Online Protection. Regularly check your mail routing settings to prevent disruptions.
What are best practices for managing a hybrid Exchange environment?
Best practices include updating regularly, monitoring actively, and using directory synchronization. Adding security measures like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC also helps protect your email system.