The AI-Driven Evolution of cybersecurity has significantly transformed the landscape. Recent statistics indicate that 74% of IT security professionals recognize a substantial impact from AI threats. Furthermore, 93% of businesses anticipate encountering daily AI attacks in the coming year. As cyber adversaries increasingly leverage AI, organizations must adapt their defenses accordingly. The average cost of data breaches has now reached $4.88 million, underscoring the urgent need for robust security measures.
The global AI in cybersecurity market is projected to expand from approximately USD 25.35 million in 2024 to USD 31.48 billion in 2025.
This growth highlights the pressing necessity for innovative strategies to combat AI-driven threats.
This evolution necessitates a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Traditional defenses are struggling to keep pace with the rapid advancements in AI capabilities.
Key Takeaways
AI is changing cybersecurity. 74% of IT workers see its effects. Companies need to change to protect against new threats.
AI attacks are quicker and smarter. They can do tasks automatically and make phishing more personal. This makes them harder to find.
Buying AI security tools can help find threats faster. This helps companies stay ahead of hackers.
AI threat intelligence helps with real-time watching and smart defense plans. This makes security better overall.
Ongoing training and rules are very important. Companies should teach workers about AI threats and update security rules often.
AI in Cybersecurity
Historical Context
The use of AI in cybersecurity started in the 1980s. This was when expert systems were created. These systems watched network traffic and found known threats. This was a big step forward in the field. Alan Turing helped lay the groundwork for early computing. He introduced important ideas like pattern recognition and logical reasoning. These ideas are still very important in today’s cybersecurity methods.
Rise of AI Technologies
AI technologies have changed how cybersecurity works. Now, organizations use machine learning to boost their defenses. Here are some key effects:
Threat Detection: Machine learning finds new threats, like polymorphic malware and zero-day exploits.
Automated Response: AI speeds up responses, helping organizations move from reactive to proactive defense.
Behavioral Analytics: These tools spot unusual behavior that might show insider threats or active attacks. This reduces false alarms and makes results more accurate.
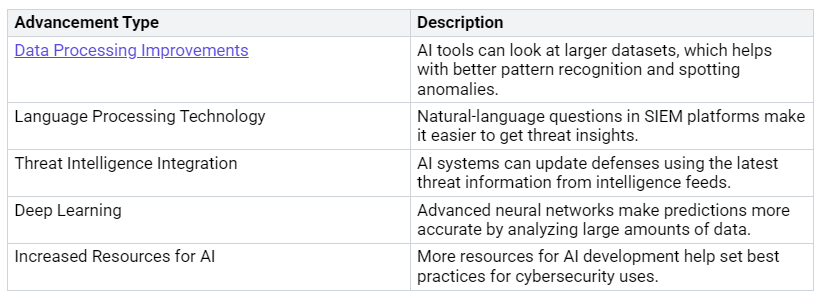
Recent tech improvements have led to more AI in cybersecurity. The table below shows these advancements:
Fields like IT and telecommunications have widely adopted AI technologies to handle cybersecurity risks. Both sectors have an adoption rate of 38%. This shows that there is a growing need for AI to protect sensitive information and keep operations running smoothly.
Nature of AI-Enabled Attacks
Characteristics of Attacks
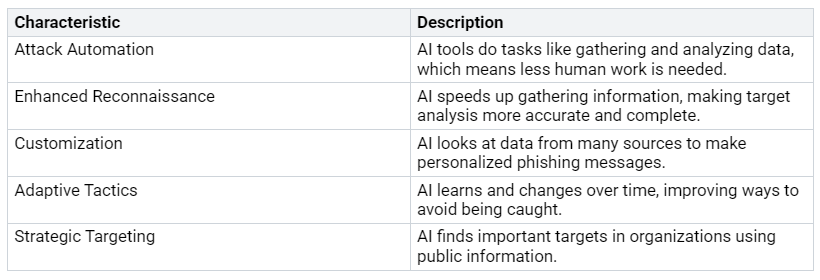
AI-enabled attacks have special traits that make them different from regular cyber threats. These attacks use automation and flexibility. This helps attackers carry out complex plans with little human help. The table below shows the main traits of AI-driven attacks:
AI-created phishing emails have a shocking 54% success rate. In contrast, traditional methods only succeed 12% of the time. Attackers can quickly make thousands of personalized phishing emails. This greatly increases the number of attacks. This ability gives more people access to advanced attack tools, making it easier for cybercriminals to strike.
Also, AI-driven attacks can happen much faster and on a larger scale. They use smart algorithms to get around traditional detection systems. They can act like humans to bypass CAPTCHAs and other security measures. This flexibility helps attackers take advantage of weaknesses more easily. As a result, regular defenses are becoming less effective.
Case Studies
Many well-known cases show how AI-enabled attacks affect organizations. These examples highlight the cleverness and success of AI-driven threats:
Deepfake Scams: One famous case involved a deepfake voice tricking an employee into giving away $243,000. This shows how dangerous AI can be in cyber fraud, as attackers can fake voices of trusted people.
Generative AI for Offense: Cybercriminals now use AI coding helpers to make malware, like remote access trojans, faster than ever. This has caused a rise in complex attacks that can hit many systems at once.
IBM’s Watson for Cyber Security: This AI system cut investigation time by 60% and reduced false positives by 30%. By using machine learning, it helped a global financial services company stop a tricky phishing attack, keeping customer data safe.
Microsoft’s Intelligent Security Graph: This platform lowered threat detection time from 24 hours to less than an hour. It improved malware detection by 40%. Its ability to analyze large amounts of data quickly helps organizations react fast to new threats.
These case studies show the real effects of AI-enabled attacks. They also highlight the urgent need for organizations to strengthen their defenses against these clever threats.
Defending Against Cyber Threats
AI-Enhanced Security
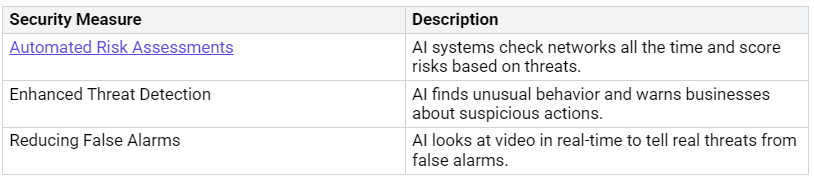
More organizations are using AI-enhanced security to fight cyber threats. These tools offer better features than regular security systems. Here is a table showing some of the best AI-enhanced security measures used by top organizations:
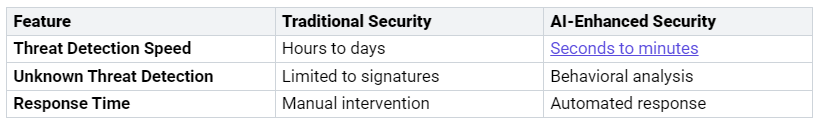
AI makes detection and response much faster than traditional methods. The table below shows the differences:
AI can process millions of data points every second. This helps find threats right away. It keeps checking network behavior to manage threats before they become serious. Automated responses cut down the time between finding a threat and acting on it. For example, AI can automatically isolate affected systems or block harmful IP addresses. This quick action helps reduce the time between spotting a threat and responding, leading to better protection.
Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence is very important for defending against AI-enabled cyber threats. It means collecting and studying information about possible threats to improve security plans. AI helps threat intelligence in many ways:
Organizations gain from ongoing learning and better management of weaknesses through AI-driven threat intelligence. This technology helps with better detection and response, making security stronger overall. AI automates how threat data is collected and analyzed, saving time and effort. Machine learning models keep improving by learning from new data.
However, organizations have some challenges when using AI-enhanced security solutions. These include worries about privacy and data protection, uneven AI performance, and the difficulty of fitting AI with current systems. Even with these challenges, the benefits of AI in threat intelligence and security are much greater than the downsides.
The AI-Driven Evolution of Defense Strategies
Future Trends
The world of cybersecurity is changing fast because of the ai-driven evolution. More organizations are using ai solutions to make their defenses stronger. Here are some important trends:
Organizations can move from just reacting to threats to predicting them. They can use real-time threat detection to look at large amounts of data and spot unusual activities quickly. This change helps them respond faster and fix problems, reducing damage from attacks.
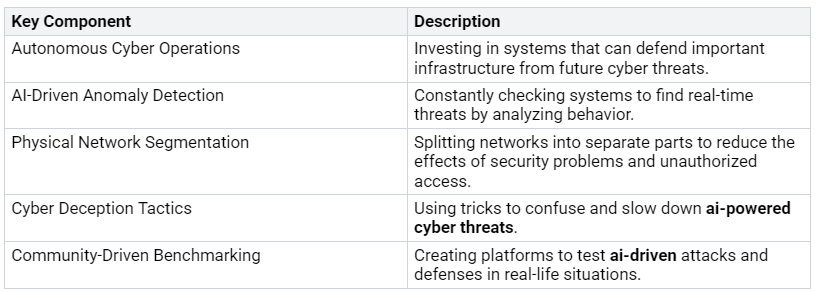
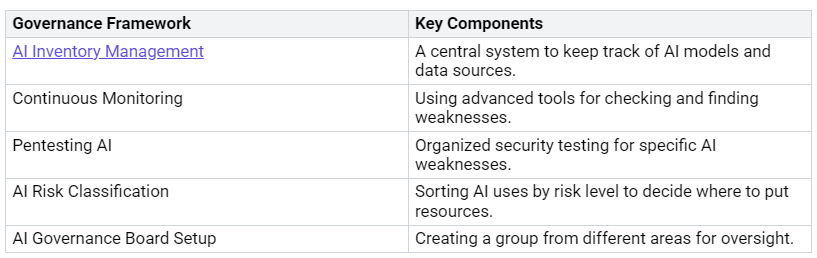
Governance and Training
Good governance and special training are very important for managing ai-driven cybersecurity systems. Organizations should set up a governance plan that includes:
Training programs need to change with the new threats. AI training makes learning more personal and helps reduce human mistakes, which often cause data breaches. Organizations should focus on:
Finding employees who do not follow good cyber practices.
Changing training based on real-time threat information.
Getting employees ready for new threats.
By investing in governance and training, organizations can improve their protection against adversarial attacks, like deepfake-driven phishing and social engineering attacks. This proactive approach makes sure teams are ready to deal with the challenges of modern cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity is changing quickly because of AI threats. Organizations are at greater risk as attackers use AI for spying, gathering information, and complex attacks. To fight these problems, businesses need to use AI tools that focus on spotting behavior patterns and analyzing threats in real-time.
Using strategies like regular updates, plans for responding to incidents, and ongoing training will make defenses stronger against AI risks. Working together across departments and improving team skills will help protect against these new threats. The time to act is now, as the future of cybersecurity relies on taking steps against AI-enabled attackers.
FAQ
What are AI-enabled cyber threats?
AI-enabled cyber threats use artificial intelligence to make attacks smarter and more effective. These threats include automated phishing, deepfake scams, and malware that can learn and change to avoid regular security systems.
How can organizations defend against AI-driven attacks?
Organizations can defend against AI-driven attacks by using AI-enhanced security tools, keeping strong basic security practices, and training employees regularly. Using threat intelligence and monitoring in real-time also helps strengthen defenses.
Why is threat intelligence important in cybersecurity?
Threat intelligence gives organizations information about possible threats and weaknesses. It helps security teams expect attacks, improve their response plans, and make overall security better by using data from different sources.
What role does employee training play in cybersecurity?
Employee training is very important in cybersecurity because it raises awareness about possible threats like phishing and social engineering. Well-trained employees can spot suspicious activities and follow best practices to reduce risks.
How does AI improve threat detection?
AI improves threat detection by quickly and accurately analyzing large amounts of data. It finds patterns and unusual activities that might show a security breach, allowing organizations to respond to threats right away and lower false alarms.